The DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL error is a recurring problem on Windows systems and manifests itself as a blue screen of death (BSOD). This critical error usually occurs when a driver attempts to access an inappropriate memory address, resulting in a violation of the system’s interrupt priorities. This malfunction prevents the Windows kernel from operating properly and forces an immediate restart of the computer.
Troubleshooting the DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL error under Windows
- What is the DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL error?
- Diagnose and resolve DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL with Windows Event Viewer
- What should I do if the problem persists after formatting?
What is the DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL error?
When a user encounters the DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL error, Windows displays a blue screen accompanied by a stop code. The message may be followed by the name of a specific file (e.g. ndis.sys, nvlddmkm.sys, ntoskrnl.exe) indicating the driver or component involved. Although this message can be intimidating, it is a valuable clue to identifying the source of the problem and resolving it effectively.
This error is often linked to the hardware drivers that ensure communication between the operating system and the computer’s physical components. If a driver malfunctions, is corrupted or is not compatible with the current version of Windows, conflicts may arise, leading to critical system instabilities.
Several factors can trigger the DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL error:
Faulty or incompatible drivers
- A recent driver update containing errors.
- Installing a driver that is not certified or not adapted to the hardware.
- A conflict between several drivers trying to access the same system resources.
Hardware problems
- A faulty or incorrectly inserted RAM memory module.
- An end-of-life hard disk with defective sectors.
- An unstable graphics or network card after an update.
Overheating and unstable power supply
- Insufficient cooling leading to excessive processor or GPU temperature.
- Poor quality power supply causing voltage fluctuations.
System file corruption
- Windows file corruption due to sudden shutdown or power failure.
- File system errors that prevent Windows from accessing drivers correctly.
- The presence of malware that alters driver operation.
Ignoring this error can lead to increasing system instability and recurring crashes. A computer affected by this type of malfunction runs the risk of being unusable in the long term, especially if the problem concerns drivers such as those for the processor, graphics card or hard disk. What’s more, each unscheduled reboot increases the risk of data loss, can damage the file system, and will make repairs more complex.

Diagnose and resolve DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL with Windows Event Viewer
The DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL error is a critical blue screen (BSOD) in Windows, usually caused by faulty drivers, hardware conflicts or failed components. When it persists despite the usual software fixes, it may indicate a hardware problem requiring replacement.
In this guide, we’ll use Windows Event Viewer to analyze system crashes and identify their origin.
The Event Viewer records all system incidents, including critical errors that may be related to BSODs.
- Open Event Viewer by pressing
Win + R, type eventvwr.msc and press Enter.
Alternatively, right-click on the Start menu and select Event Viewer.
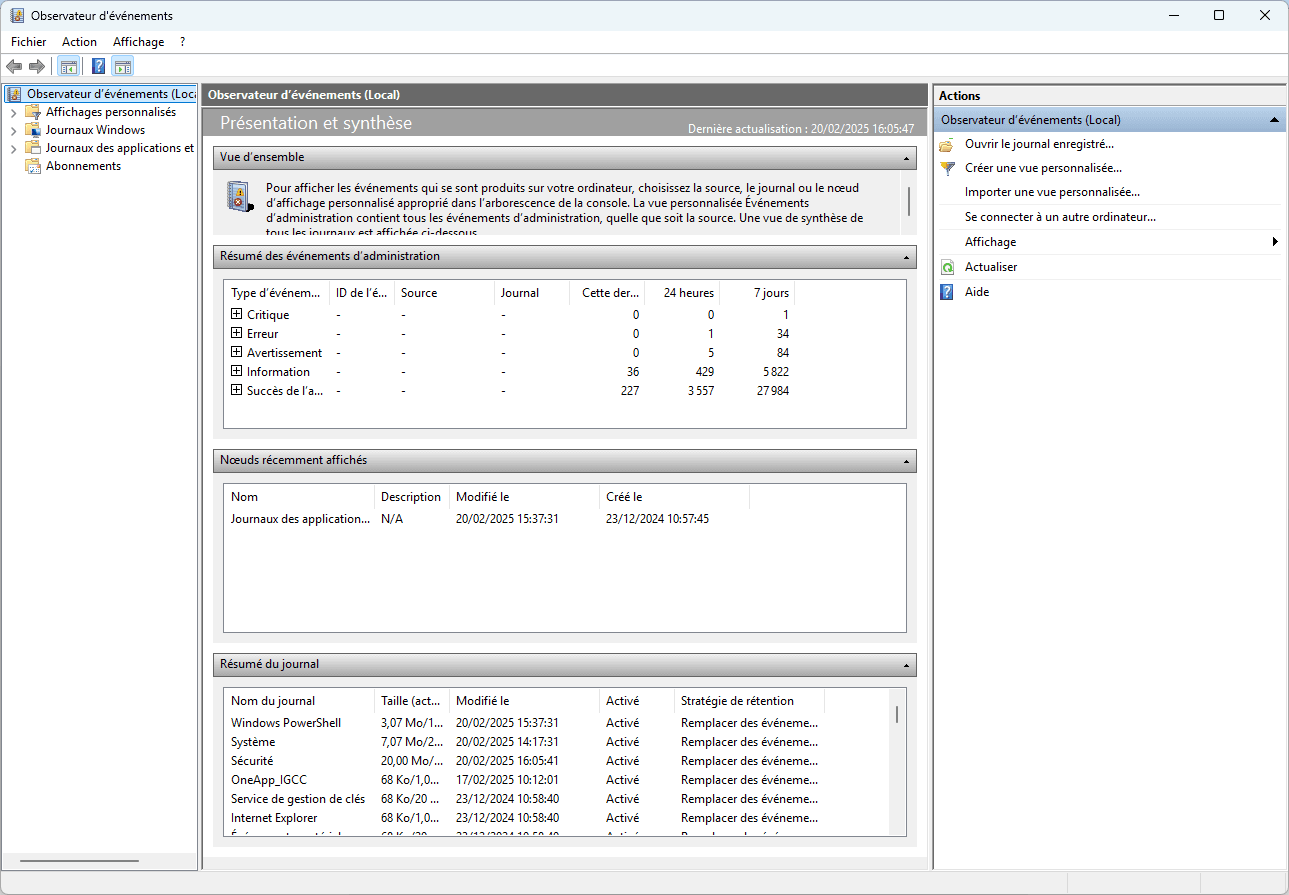
- Go to Windows Logs > System.
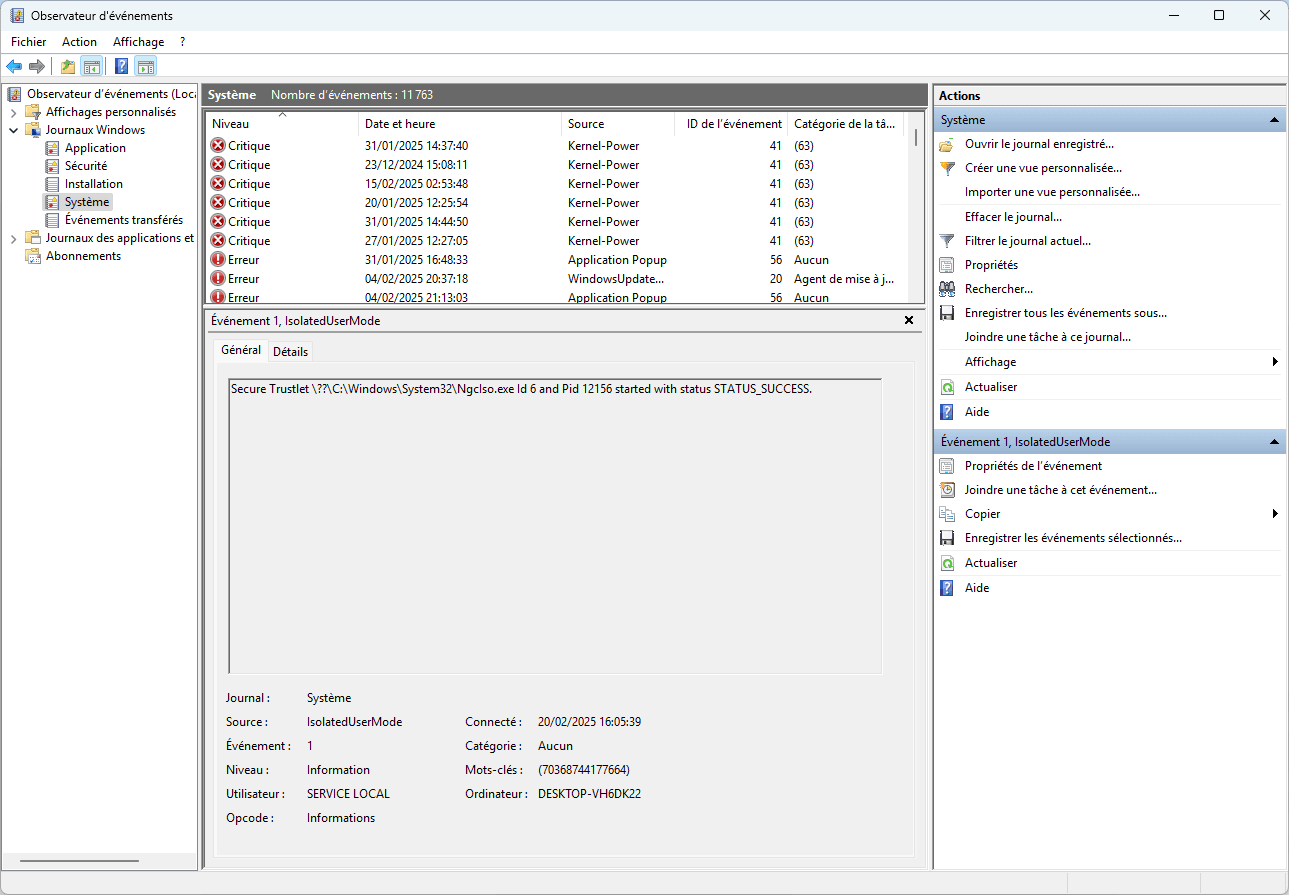
- Filter critical or error-related events Kernel-Power, BugCheck.
- Check stop codes and drivers.
These analyses help identify whether the error stems from a particular driver, a hardware problem or software instability.
When the error is accompanied by a specific file, this gives an indication of the origin of the problem:
| Involved file | Associated component | Possible problem |
|---|---|---|
| ndis.sys | Network driver | Conflict with network card, corrupt driver |
| nvlddmkm.sys | NVIDIA driver | Incorrect installation or update of graphics driver |
| ntoskrnl.exe | Windows kernel | Memory problem or system corruption |
| usbport.sys | USB driver | Faulty USB device or obsolete driver |
| atikmdag.sys | AMD driver | AMD graphics driver incompatibility or crash |
- Update or reinstall the driver concerned
- Test linked peripherals (power supply, graphics card, network, USB, etc.)
- Check system file integrity with
sfc /scannow
By carrying out this analysis, it is possible to precisely identify the cause of the error and take the appropriate measures to prevent the problem recurring.
What should I do if the problem persists after formatting?
If the DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL problem persists after a full system reinstall, this is most likely an indication of a critical hardware failure.
A clean reinstallation of Windows eliminates any possibility of software corruption or faulty drivers. If the error continues to occur, it means that one of the computer’s components is severely damaged and causing system downtime.
The elements most likely to be involved are :
- RAM: defective modules causing memory access errors.
- The processor (CPU): poor interrupt handling due to overheating or electrical instability.
- Motherboard: chipset or PCI line faults causing hardware conflicts.
- Power supply: unstable voltages causing irregular errors.
- The hard disk or SSD: Read/write errors affecting the correct loading of drivers and the Windows kernel.
In this case, we recommend a thorough hardware diagnosis, testing each component individually. If a fault is detected, it will be necessary to replace the component in question to restore a stable system.
Find all our Windows tips and tutorials on our computer blog.