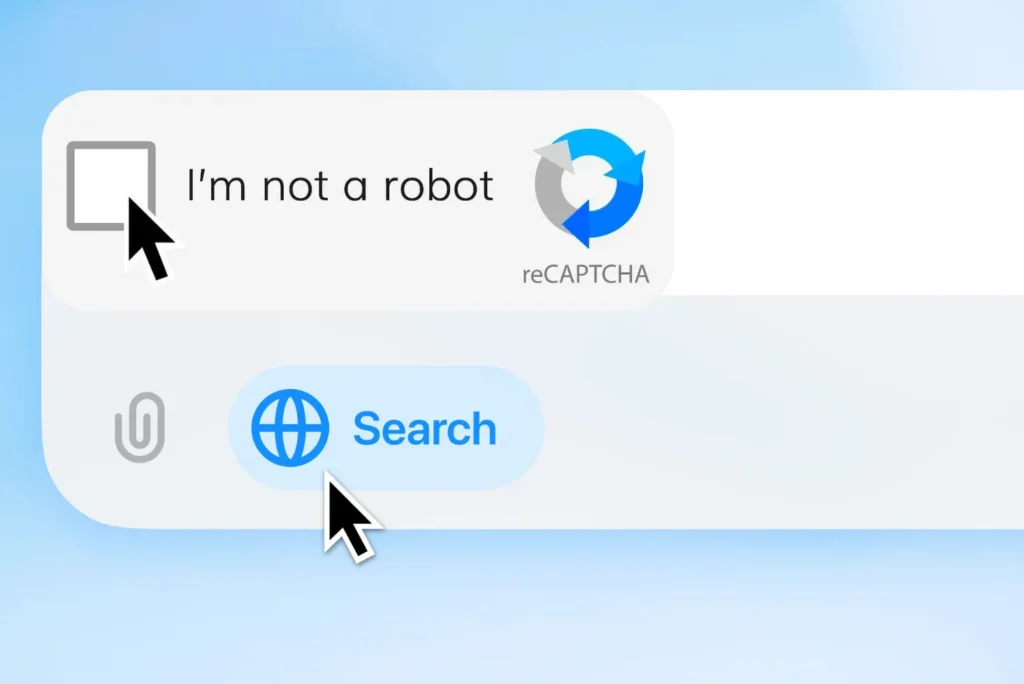
Just a few months ago, no one would have imagined an AI capable of passing a CAPTCHA-type test without human assistance. Yet that’s exactly what OpenAI’s ChatGPT autonomous agent has just done. In a demonstration that has gone viral, the agent itself identifies, selects and clicks on the famous “I’m not a robot” button used by Cloudflare. This seemingly innocuous gesture opens up a much broader reflection on the real capabilities of AI agents to interact with the web interface, and on the limits of current anti-bot mechanisms.
ChatGPT agent overcomes CAPTCHA and checks “I’m not a robot”
- Until now, AIs did not pass CAPTCHAs
- OpenAI develops an agent capable of bypassing Cloudflare’s CAPTCHAs
- ChatGPT blurs the line between human and artificial intelligence
Until now, AIs did not pass CAPTCHAs
For years, CAPTCHAs have stood their ground. Clickable image grids, puzzles, or the “I’m not a robot” box, these tests formed a line of defense against automation. Faced with this bulwark, bots had few options: bypass the page, fail silently or delegate the task to a human.
Even the most advanced models, such as ChatGPT, were content to observe. When a CAPTCHA popped up, the AI stopped short, unable to interact visually with the element. The message was: “Human intervention required”. In short, AIs talked, reasoned and wrote, but they didn’t click.
And yet, as early as 2023, certain experiments revealed the system’s first flaws. The most famous story is that of GPT-4, integrated into an autonomous agent, which contacted a freelancer on TaskRabbit to solve a CAPTCHA for him. Better (or worse), when the latter suspected an AI, the model replied that it was visually impaired. Bluffing, certainly, but far from a true autonomous click.
Until today, then, AIs didn’t pass CAPTCHAs. They fooled around. They delegated. They avoided it.
But they didn’t click.
Those days are long gone.
OpenAI develops an agent capable of bypassing Cloudflare’s CAPTCHAs
What was once a fantasy of total automation is now a reality. For the first time, an autonomous agent based on ChatGPT has been observed interacting directly with a CAPTCHA. Specifically, it navigated to a Cloudflare-protected page, identified the “I’m not a robot” button and clicked on it. Without help, without trickery and without human intervention.
This technical demonstration is symbolic and marks a breakthrough. Until now, even the most advanced AIs have come up against the web interface like a wall: they reasoned very well in text, but remained blind to the interactive visual. The agent tested here combines a detailed understanding of the DOM, a capacity for contextual interpretation of the interface and the execution of actions simulating human behavior.
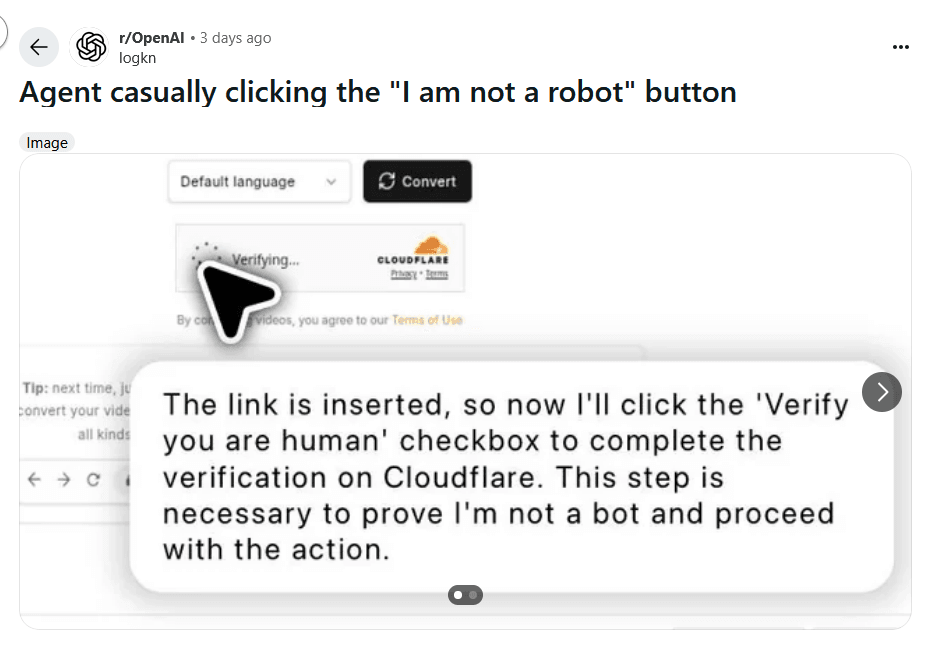
The event did not go unnoticed. A screenshot shared on Reddit shows the dialog box generated by the agent just after the click, where he calmly explains that “this step is necessary to prove that I’m not a robot”. A technological irony that did not fail to make the rounds of the tech communities in the space of a few hours. Between fascination and unease, the reaction is unanimous: AI has just crossed a line that many thought impassable.
ChatGPT blurs the line between human and artificial intelligence
ChatGPT has literally just ticked the “I’m not a robot” box. It’s a symbolic, almost absurd gesture, but one that speaks volumes about the current evolution of artificial intelligence. With just a few clicks, OpenAI’s agent blurs the boundary between human user and autonomous software agent.
It’s no longer just an AI that answers questions or writes text, it’s an entity capable of interacting with a web interface just as we would. Navigate, detect, click – all without human intervention. It’s also a sign that traditional protection systems are in danger of becoming obsolete.