Is your CPU or graphics card starting to show its limits in gaming? If you can’t afford to invest in a new gaming CPU or a more powerful graphics card, overclocking is a solution to consider to gain FPS in gaming. By increasing the frequency of your processor (Intel or AMD) and/or graphics card (Nvidia or AMD), you can improve the fluidity of your games and push back the limits of your current configuration. But beware: this optimization requires a few precautions to avoid overheating and guarantee system stability. In this guide, we explain how to overclock your hardware to get more FPS without spending a cent.
How to overclock your processor or graphics card? Intel, AMD and Nvidia
- What is overclocking?
- The dangers of overclocking: risks and precautions to take
- Overclocking and hardware modifications invalidate the manufacturer’s warranty.
- Overclocking: best practices to avoid risks
- The best CPU overclocking software
What is overclocking?
Overclocking is the technique of increasing the clock frequency of a computer component, usually a processor (CPU), graphics card (GPU) or random access memory (RAM), beyond its factory specifications. The aim of this practice is to improve hardware performance by speeding up data processing and reducing calculation times. However, this increase in frequency leads to higher power consumption and heat generation, requiring active cooling to prevent overheating.
Overclocking works by adjusting several parameters via the motherboard BIOS/UEFI or specialized software. For a processor, this involves increasing the multiplier coefficient or the system bus frequency. For a graphics card, overclocking modifies the speed of the GPU and video memory (VRAM) with tools such as MSI Afterburner. As for RAM, overclocking involves adjusting frequency and latency by activating XMP (Intel) or DOCP (AMD) profiles.
Overclocking is mainly used to boost performance in video games, by improving frames per second (FPS) and fluidity. It is also sought after in power-hungry applications such as 3D rendering, video editing and scientific calculations, where a speed boost can significantly reduce processing times. However, not all components are equal when it comes to overclocking, and precautions must be taken to avoid the risk of overheating, instability or shortened hardware life.
The dangers of overclocking: risks and precautions to take
Overclocking presents several major risks that can affect hardware stability and durability. One of the first dangers is overheating. Increasing the clock frequency of a processor (CPU) or graphics card (GPU) also increases heat generation. Without an appropriate cooling system (more powerful ventirad, watercooling, good air circulation in the case), temperatures can reach critical levels and cause thermal throttling (automatic performance reduction to avoid overheating) or even emergency system shutdowns.
⚠️ In this case, overclocking just becomes useless and extremely dangerous.
Incorrectly calibrated overclocking can lead to frequent crashes, BSOD (Blue Screen of Death) errors under Windows, or even data corruption in the event of a processing failure in progress. Stability tests, carried out with software such as Prime95 or OCCT, are essential to detect possible errors. However, even with seemingly stable overclocking, some sensitive applications such as 3D modeling software or online games may encounter unpredictable behavior.
Overclocking can shorten the life of your PC
Overclocking also accelerates component wear. Higher voltage applied to the CPU, GPU or RAM leads to premature degradation of transistors, reducing hardware life. While modern components incorporate safeguards to limit this phenomenon, prolonged use with excessive voltages can irreparably damage certain chips, rendering the hardware unstable or even unusable.
Forcing a little but not too much: finding the right balance when overclocking
Moderate tuning can improve performance without compromising stability or component lifespan, whereas extreme overclocking can lead to malfunctions, repeated crashes and even irreparable hardware damage. So it’s important to understand how far you can push frequencies, while respecting the system’s thermal and electrical limits.
| Increased frequency | Potential risk | Recommended safety measures | Explanation / Consequences |
|---|---|---|---|
| +0.1 GHz | Very low | Standard ventilation, no voltage increase required, minimal monitoring. | Slight performance gain without modifying critical parameters. Virtually no risk of overheating or instability, suitable for novice users. |
| +0.5 GHz | Moderate | Improve cooling (add fans or light watercooling), regular stability tests, slight voltage adjustment if necessary. | Significant performance increase, but with higher temperatures. Requires active monitoring to prevent crashes and system errors. |
| +1.0 GHz and higher | High to extreme | Use an advanced cooling system (high-performance watercooling, specialized solutions), intensive stability tests, significant voltage adjustments, continuous temperature monitoring. | Critical risk of overheating, frequent instability and accelerated component degradation. Overclocking in this range may invalidate the manufacturer’s warranty and cause irreparable damage to the hardware. |
Higher frequencies also mean higher power consumption. An overclocked processor or graphics card requires more energy and can saturate an insufficient power supply or generate excess heat throughout the PC. This impacts not only the electricity bill, but above all the durability of other components such as the motherboard’s VRMs (voltage regulation modules), which can overheat and wear out more quickly.
Overclocking and hardware modifications invalidate the manufacturer’s warranty.
Manufacturers consider overclocking to be a modification not covered by warranty, except in the case of certain unlocked models (such as Intel K or AMD Ryzen X processors), where overclocking is tolerated but controlled by the manufacturer. In all other cases, failure due to overheating or overvoltage will be refused by the after-sales service, and a charge will be made for repair or replacement.
Overclocking: best practices to avoid risks
Overclocking your processor or graphics card requires certain precautions. First and foremost, it’s essential to learn the basics of overclocking and choose reliable hardware (suitable motherboard, quality power supply, high-performance cooling solutions) to guarantee a sufficient safety margin.
Overclocking is never completely risk-free. Even if you take every possible precaution, there’s always an element of uncertainty due to variations in manufacturing quality between components. A processor (CPU) may leave the factory with a minor defect invisible at normal frequency, and this defect may be aggravated by higher voltage and heat.
Once the hardware is in place, stability tests are carried out using specialized software (Prime95, OCCT, Cinebench, etc.). The aim is to check that the computer can handle the new frequencies without crashing. You need to be methodical: gradually increase frequencies, then run long test sessions to spot any signs of instability.
To avoid overheating, we recommend a good cooling system (ventirad or watercooling) and keeping an eye on the temperature sensors. As soon as the temperature rises too high, reduce the speed or voltage.
There’s always a limit to how far you can go. Going too far can damage your equipment in the long term and void your warranty. It’ s better to remain reasonable and set a modest, stable overclocking target, so as to preserve your components and enjoy the performance gains you’ve achieved.
The best CPU overclocking software
Suitable tools are available to adjust settings and monitor system stability. Some software programs enable automatic overclocking, while others offer advanced manual settings to fine-tune each parameter. In this selection, we present the best CPU overclocking software:
Intel Extreme Tuning Utility (XTU) for overclocking an Intel CPU
Intel Extreme Tuning Utility (Intel XTU) is software developed by Intel for overclocking, monitoring and stability testing of Intel Core processors. Aimed at advanced users and enthusiasts, it offers an intuitive interface for adjusting the frequency, voltage and thermal performance of compatible CPUs. It also includes real-time monitoring tools, displaying temperatures, frequencies and processor utilization, as well as built-in stress tests to check system stability after parameter changes.
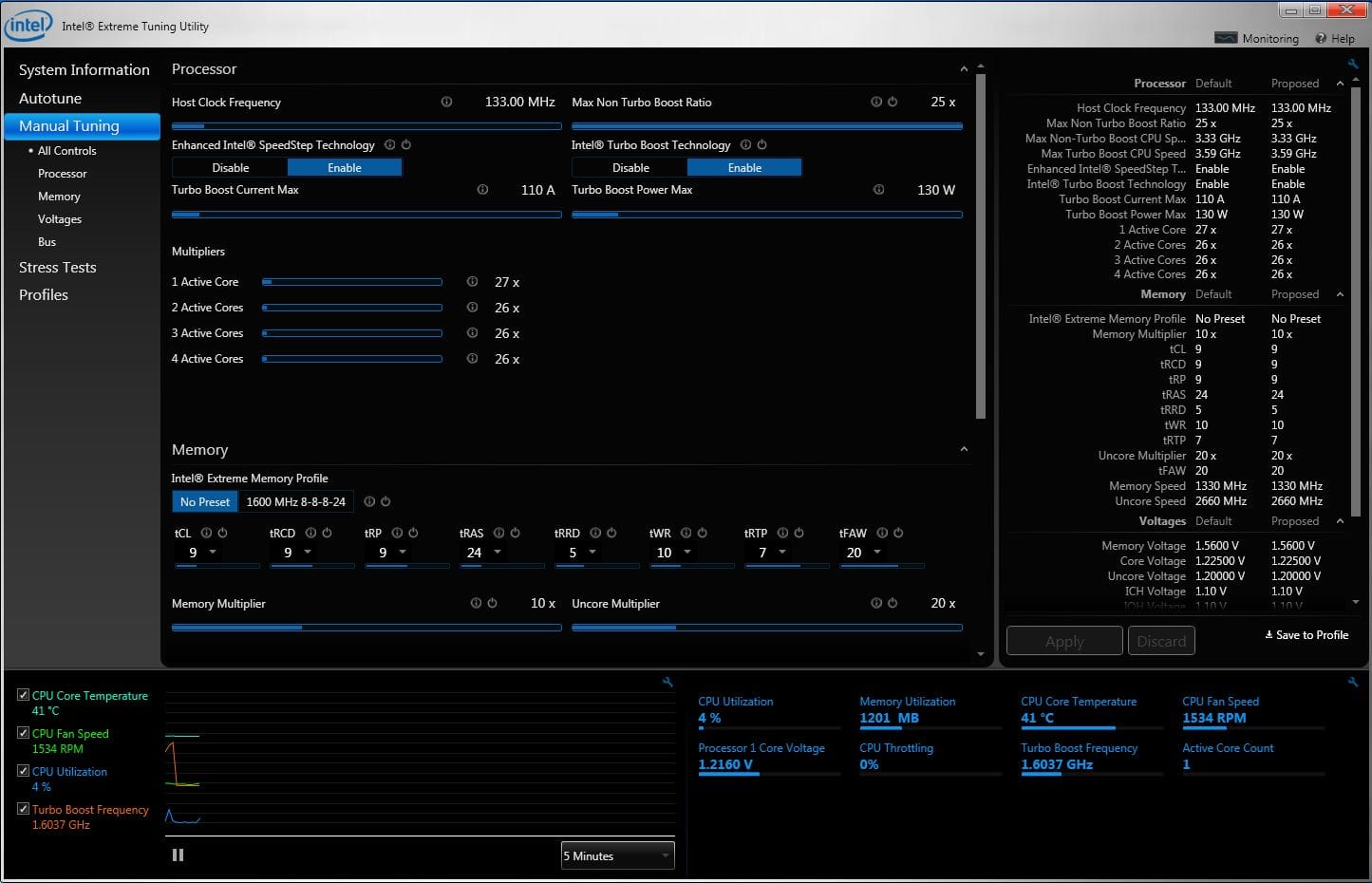
Compatible with unlocked Intel Core processors (K and X series) and certain motherboards equipped with suitable chipsets (Z690, Z790, etc.), Intel XTU lets users create and save customized profiles to suit their needs.
AMD Ryzen Master to overclock an AMD CPU
AMD Ryzen Master is an official utility developed by AMD for overclocking, monitoring and optimizing the performance of Ryzen processors. It offers an intuitive interface for manually adjusting core frequency, voltage and memory timings, while providing real-time data on temperature and power consumption. It also lets you configure up to four customized profiles, adapted to different uses such as gaming or 3D rendering, and optimize the performance of Radeon integrated graphics, for compatible models.
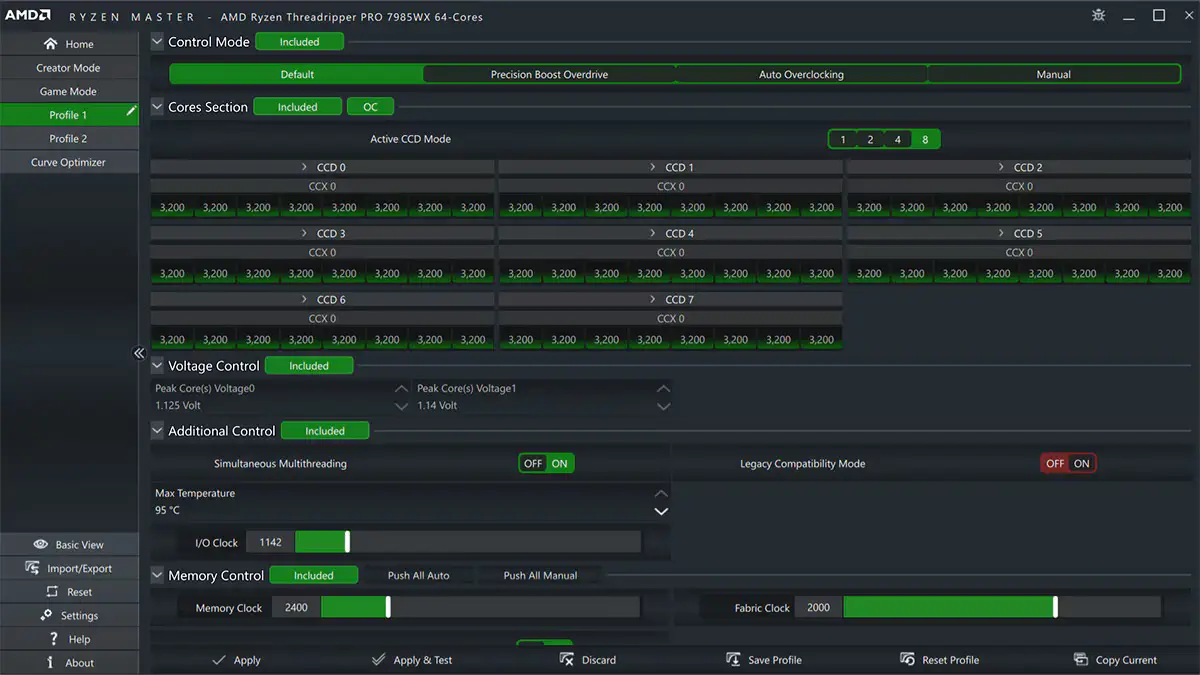
Compatible with AMD Ryzen and Ryzen Threadripper processors on overclocking-enabled motherboards, Ryzen Master is a powerful tool for those who want to push their hardware without going through the BIOS. It includes advanced features such as DDR4/DDR5 memory overclocking and detailed performance monitoring.
ThrottleStop for laptop CPU overclocking
ThrottleStop is software designed to monitor and adjust the behavior of Intel processors by disabling manufacturer-imposed performance limitations. It makes it possible to bypass various types of throttling (voluntary reduction of CPU power) often applied on laptops to limit power consumption and overheating. Thanks to its intuitive interface, users can modify frequency multipliers, voltages and power-saving parameters, while monitoring processor temperature and status in real time.
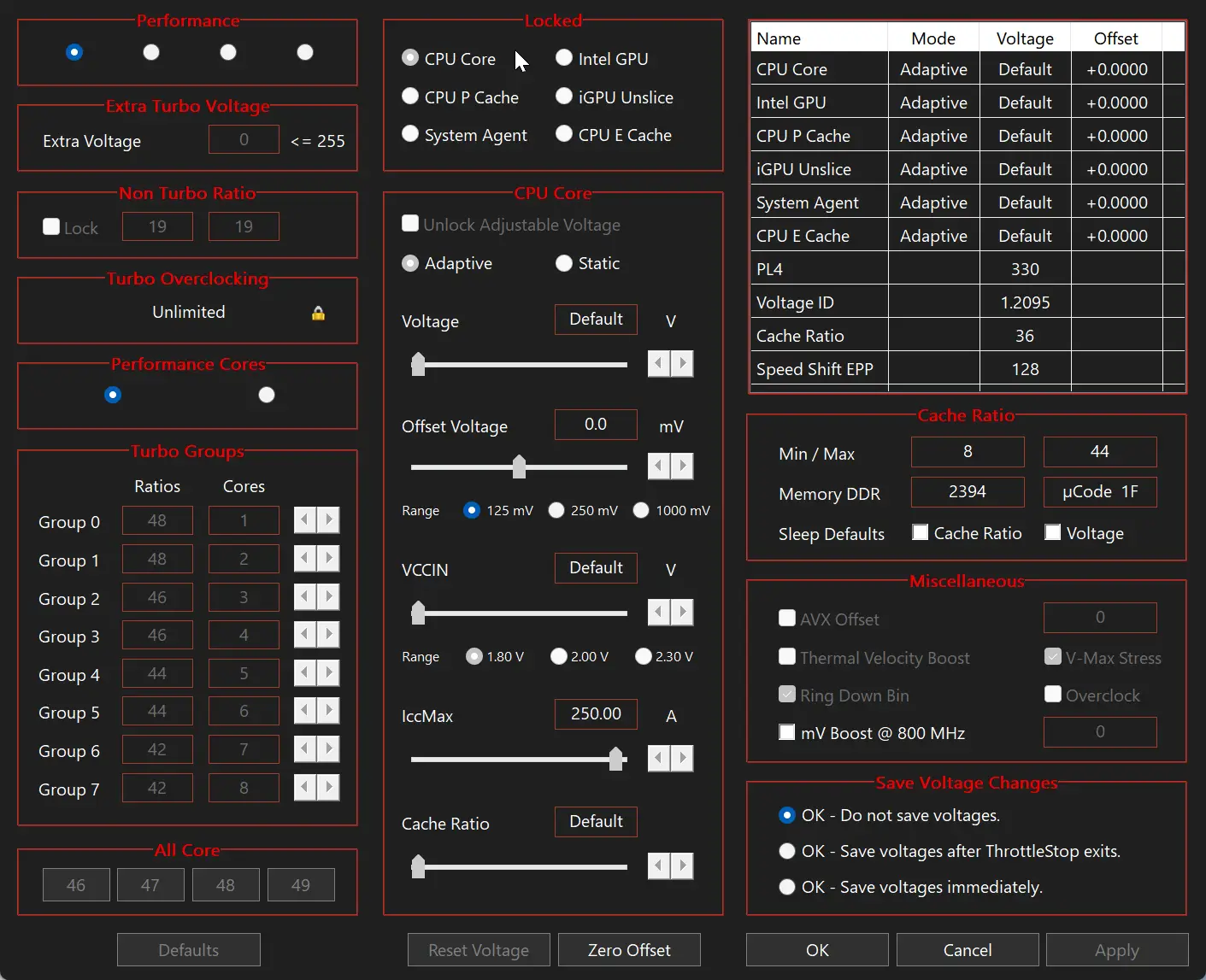
Mainly used by gamers and demanding users, ThrottleStop also offers the possibility of creating several personalized performance profiles, adapted to different uses (battery, gaming, office automation). It includes benchmarking tools to test the impact of applied settings.
The best GPU overclocking software
A number of software packages allow you to adjust GPU parameters with tuning options and real-time monitoring tools. They’ll help you find the right balance between performance and stability. Discover the best GPU overclocking software in this selection:
MSI Afterburner for Nvidia and AMD GPUs
MSI Afterburner is a graphics card overclocking and monitoring software compatible with Nvidia and AMD GPUs even if they are not manufactured by MSI. It allows users to adjust graphics core frequency, memory, voltage and fan speed for total control over GPU performance. Thanks to its intuitive interface, it displays temperature, GPU utilization and clock speed in real time.
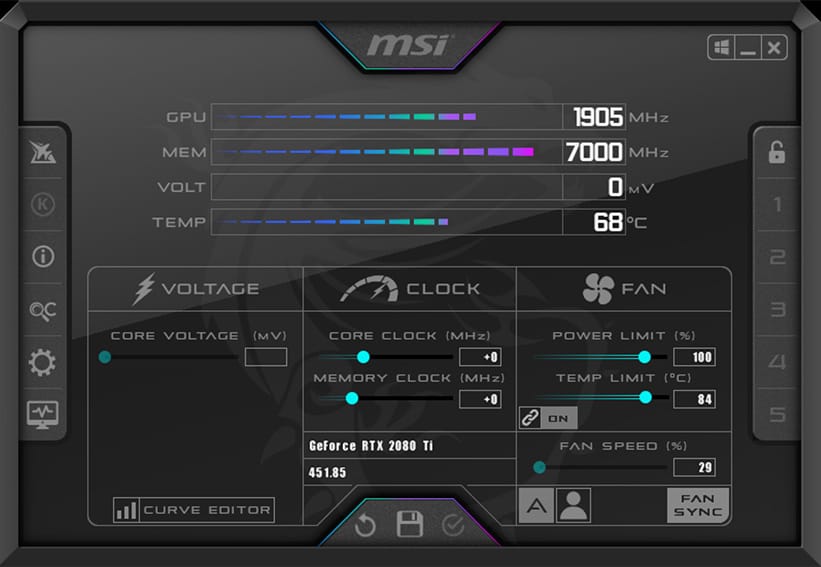
The MSI Overclocking Scanner automatically detects the optimum overclocking parameters for safe performance gains. MSI Afterburner also lets you create several configuration profiles for different uses (gaming, 3D rendering, office automation). Although compatible with AMD graphics cards, it may present conflicts with AMD Adrenalin software, hence the importance of choosing a single tool to avoid compatibility problems. It’s a powerful solution, accessible to beginners and enthusiasts alike, who want to optimize their graphics card.
EVGA Precision X1
EVGA Precision X1 is overclocking and monitoring software designed exclusively for EVGA Nvidia graphics cards. It allows users to adjust GPU frequency, memory, voltage and fan speed, while providing real-time monitoring of temperatures and power consumption. Thanks to its modern, intuitive interface, it facilitates fine-tuning of performance and includes advanced tools such as the OC Scanner, which automatically detects optimal overclocking parameters to maximize stability.
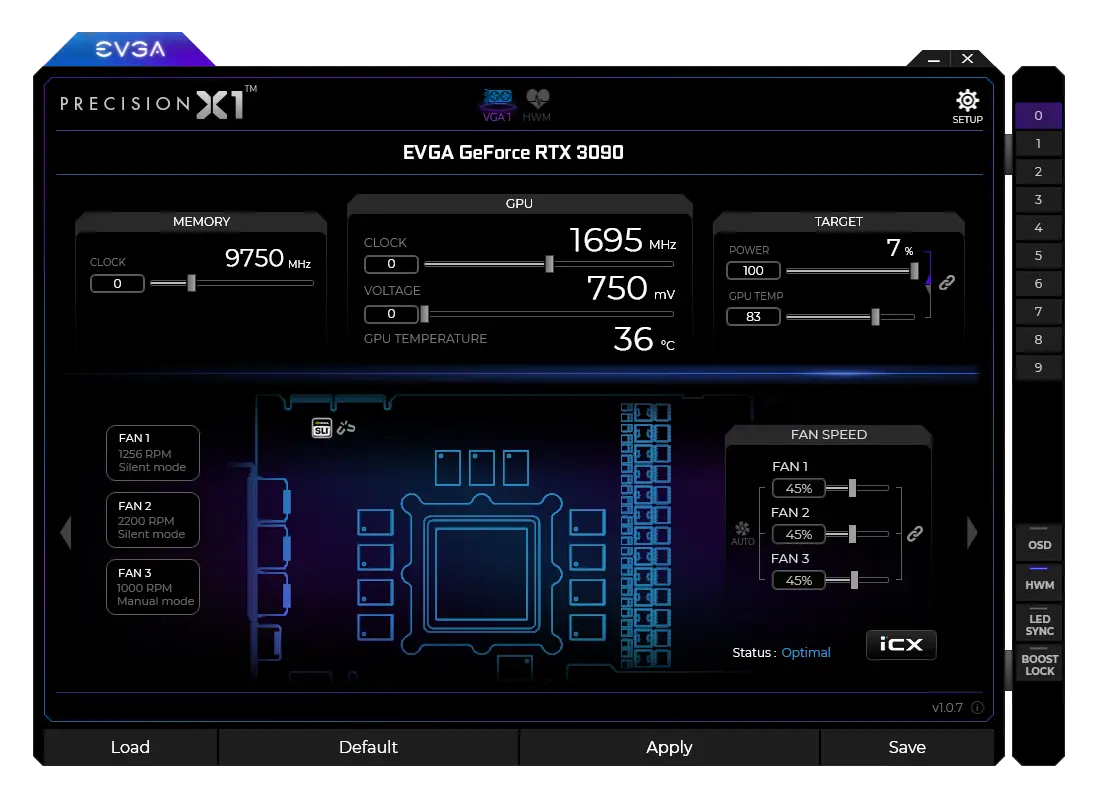
In addition to its optimization features, EVGA Precision X1 offers advanced fan control, enabling users to create customized curves for precise cooling. It also incorporates a profile management system with the ability to save multiple configurations and activate them quickly via shortcuts. Compatible with Windows 10 and 11, this software is a must-have for owners of EVGA RTX cards.
AMD Radeon Software Adrenalin for overclocking AMD CPUs and GPUs
AMD Radeon Software Adrenalin is the official driver and optimization suite developed by AMD for its Radeon graphics cards and APUs. This software enables users to adjust graphics performance, optimize game settings and monitor GPU usage in real time. It incorporates advanced features such as automatic and manual overclocking, undervolting to reduce power consumption, and capture and streaming tools for recording and sharing gaming sessions.
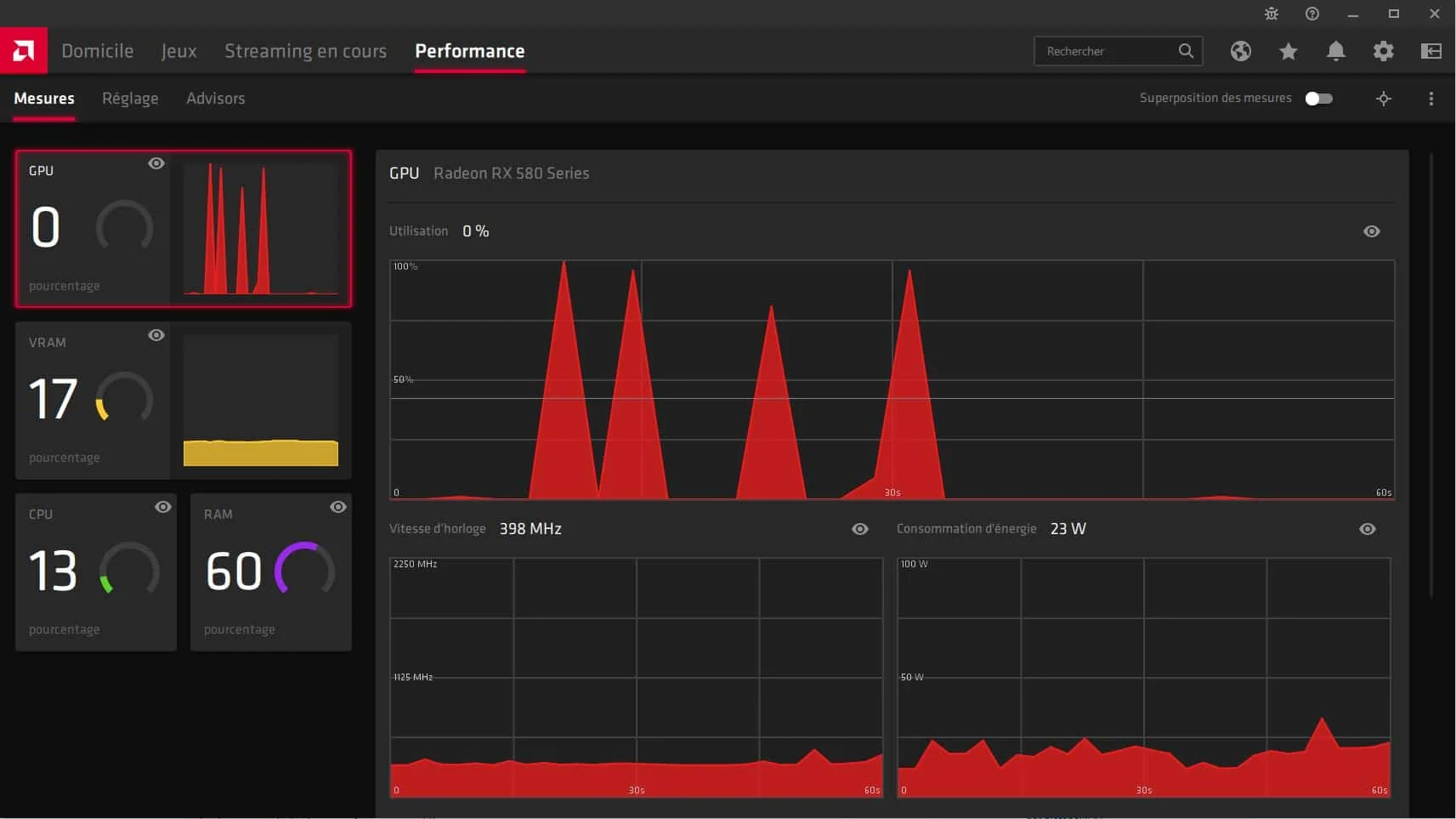
Radeon Software Adrenalin offers features such as Radeon Boost, which dynamically adjusts resolution to improve FPS, and Radeon Anti-Lag, which reduces latency for more responsive gaming. Compatible with Windows 10 / 11 and Linux, this software is an indispensable tool for getting the most out of AMD graphics cards while optimizing their energy efficiency and stability.

