When you plug an external hard drive into your computer, you expect it to appear instantly in File Explorer. Yet sometimes nothing happens, no sound, no message, no sign of life. This silence can be confusing, but it doesn’t necessarily mean a serious failure. In most cases the issue comes from a simple drive letter conflict, a missing partition, or a faulty driver. This article walks you step by step through understanding why your drive isn’t detected in Windows and how to make it visible again.
How do I get a hard disk that is not recognized or invisible in Windows?
- Identify the cause of the problem
- 1. Assign a drive letter to your external hard drive
- 2. Formatting and initializing a hard disk under Windows 11
- Test the disk in another environment
- Recovering data before repair or formatting
Identify the cause of the problem
Before changing anything in Windows, it is essential to determine whether the problem comes from the system or the hardware itself. In many cases, an undetected hard drive is not caused by a complex failure but by a simple connection or power issue. Start by ruling out the most obvious causes before considering software troubleshooting.
Start with essential hard disk checks
An external hard drive needs a stable power supply and a USB connection to function properly. If one of these elements is missing, it may become invisible in Windows. Start by disconnecting and reconnecting the USB cable, making sure it’s firmly inserted on both sides. Then try another USB port, preferably on the back of your computer, as these ports are more stable than those directly connected to the motherboard.
A faulty cable is a common cause, so replace it with another compatible USB cable, or borrow one from another drive to cross-test. Finally, listen carefully to your drive: a slight spinning noise indicates that the motor is running, while a repetitive clicking or complete silence may reveal a mechanical failure. In this case, avoid repeated testing to avoid aggravating internal damage.
Listening to the disc also provides valuable information. A slight, regular whirring generally indicates normal operation, while repeated clicking or complete silence may reveal a mechanical blockage. In this situation, it’s best to stop plugging in immediately to avoid further damage to the internal platters.
1. Assign a drive letter to your external hard drive
A hard disk may be recognized by Windows but not appear in File Explorer. This happens when the system fails to assign a drive letter. In this case, all you have to do is set the drive letter manually to make the drive accessible again. Here’s the complete procedure, step by step.
- Go to Control Panel and click on System and Security.
This section contains the main tools for system maintenance and management.
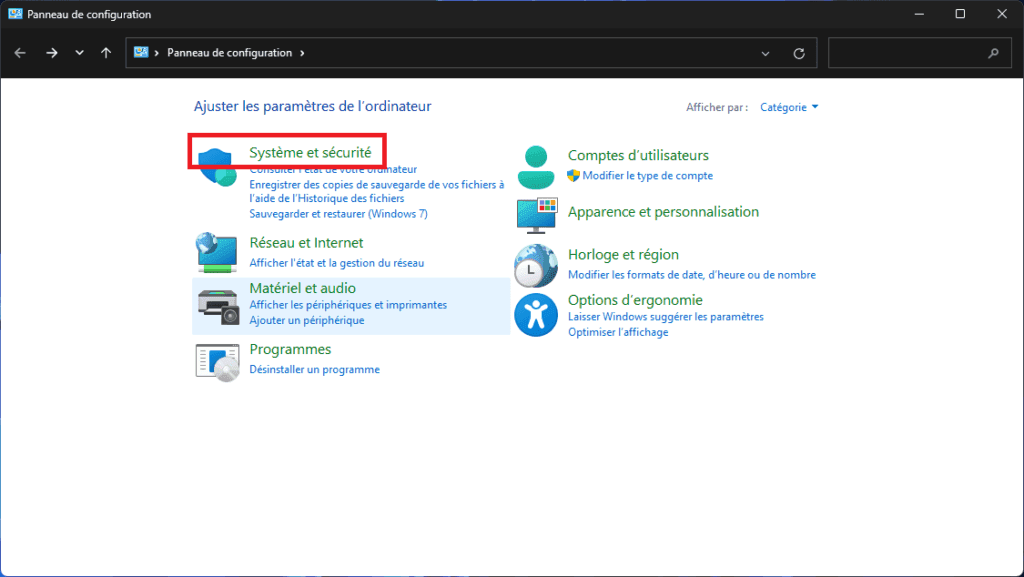
- In the options provided, click on Create and format hard disk partitions. This command opens the Disk Management utility, an integrated Windows module that displays a complete list of storage media connected to your computer.
Here you can view your internal drives, USB sticks and external disks, whether or not they are visible in Explorer.
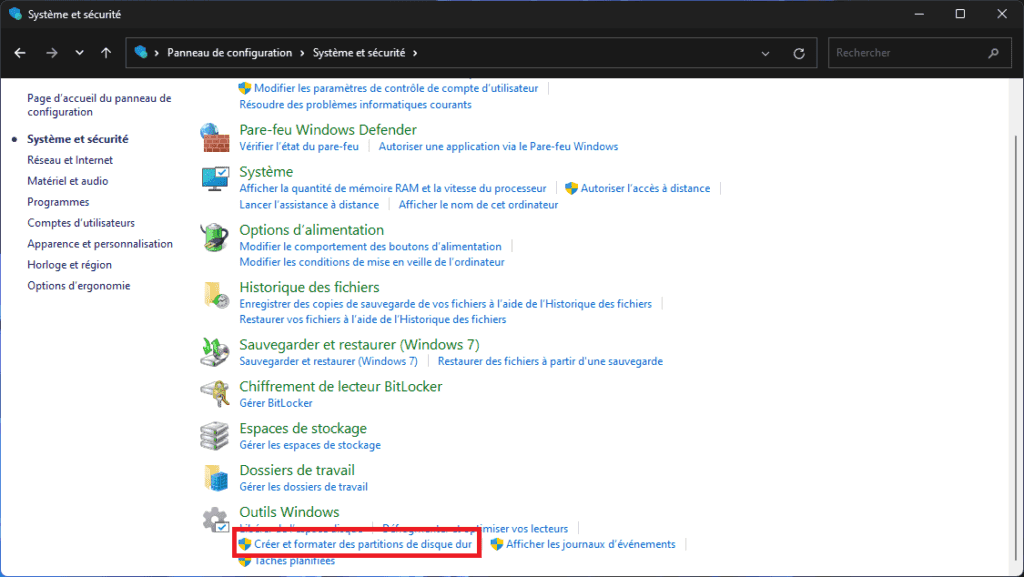
In the lower part of the window, locate your external hard drive. If detected correctly, it will appear with its name, capacity and status.
- Then right-click on the hard disk in question, and click on Modify drive letter and paths…
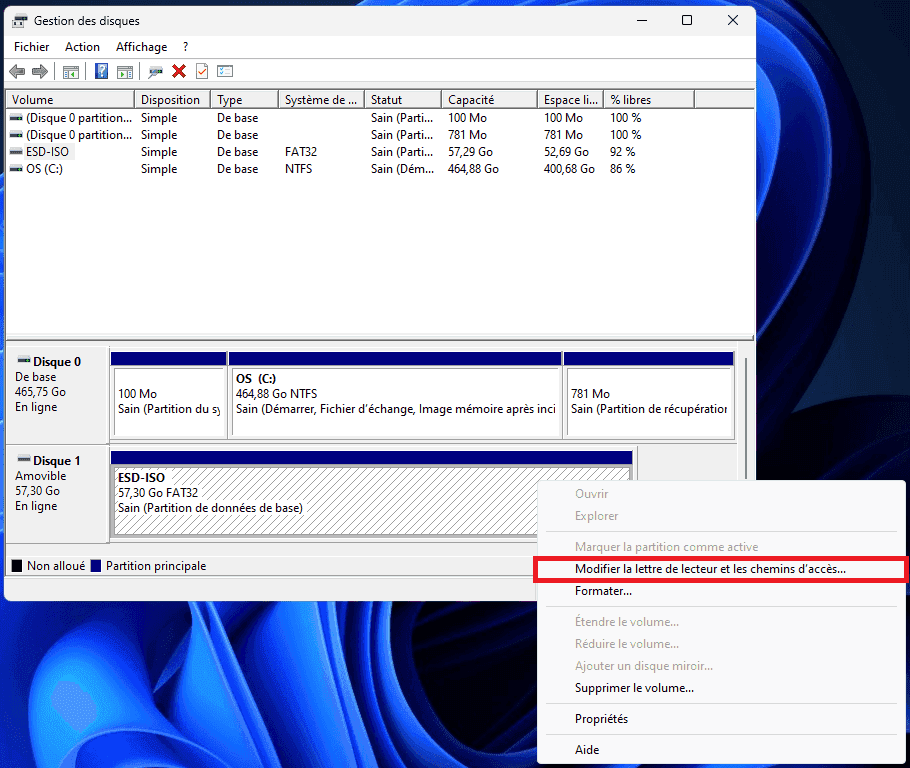
A small window opens with the letters already assigned, if any. This is where you can add or modify the letter associated with your disk.
- Click on Add, then select an available letter from the drop-down menu.
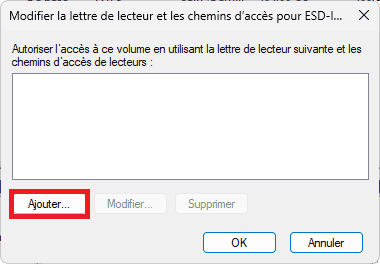
- You can choose any unused letter. Then confirm your choice by clicking OK. Windows immediately applies the change and updates the volume list.
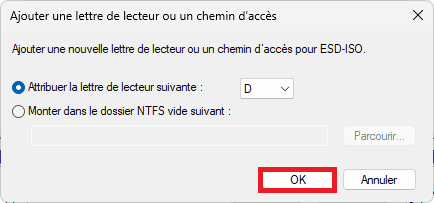
Open a new Explorer window. Your external hard drive should now appear in the left-hand column, along with the letter you’ve just assigned to it. It is now fully accessible and ready to use.
This operation in no way modifies the data on the disk. It simply gives it an identity in the system, so that it can be recognized by Windows. In many cases, this simple operation is enough to solve a non-detection problem and instantly restore access to your files.
2. Formatting and initializing a hard disk under Windows 11
When Windows detects a disk but is unable to open it, it may not yet have been initialized, or it may need to be formatted before it can be used correctly. These operations involve preparing the disk so that the system can store files on it.
- Go to Control Panel and click on System and Security.

- From the available options, select Create and format hard disk partitions.
This command opens Disk Management, a Windows-integrated tool that lets you view all your storage devices.

- Right-click on the hard disk in question, then click on Format….
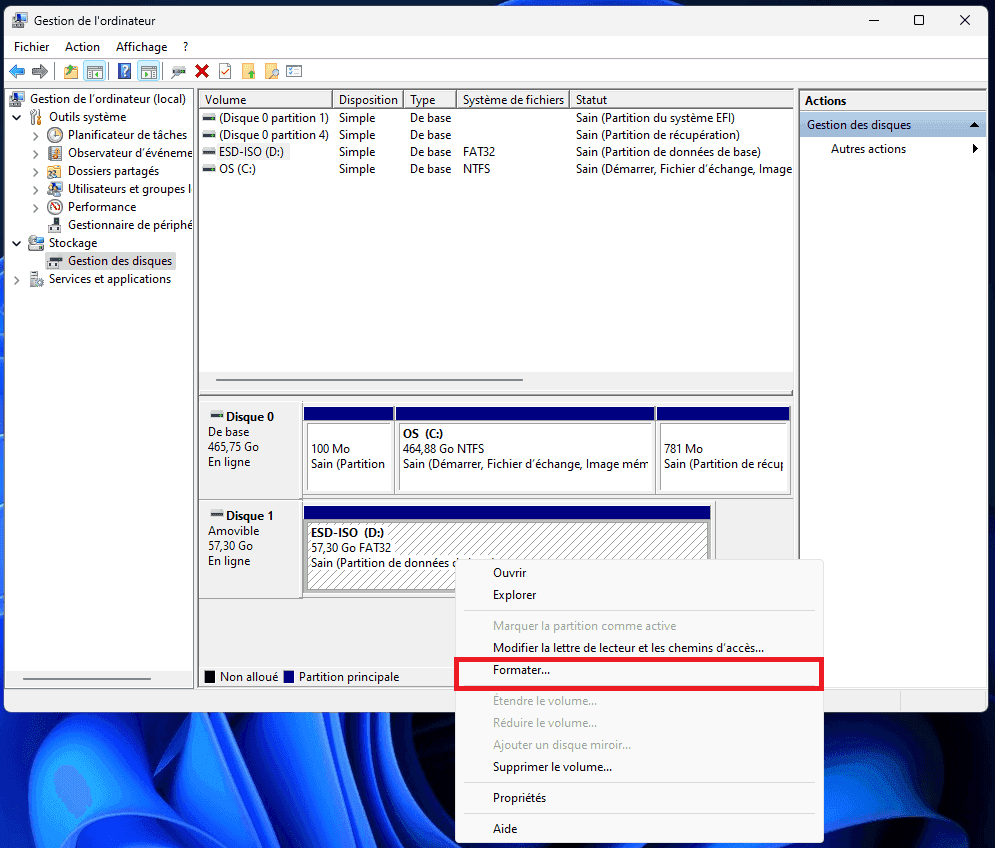
- You can then give the hard disk a new name and click OK.
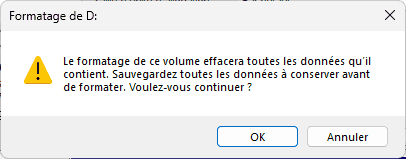
- A warning appears, to avoid handling errors and data loss, click OK.
The process takes just a few seconds for an empty disk, or a few minutes depending on its capacity. Once complete, the volume appears in the list, indicating that it is ready for use. You can then close the window and open File Explorer to check that the disk is now visible and accessible.
Formatting and initializing a hard disk is a fundamental step in preparing a new medium, correcting a partition problem or resetting an unusable volume. This operation allows you to start again from a sound base.
Find out how to permanently erase data from an external drive.
Test the disk in another environment
If all hardware checks prove unsuccessful, it is necessary to test the disk in another environment to determine whether the fault really originates from the hardware or the operating system. If the disk is recognized elsewhere, the hardware is sound and the problem is due to software configuration, a driver or an internal system conflict.
If this is not the case, it may be useful to test the disk outside Windows, using a bootable Linux key. These independent environments enable you to check whether the hardware is detected at hardware level, confirm that the hardware is in good condition and that the problem lies with the system or partition format.
Recovering data before repair or formatting
Not all hard disk failures are lost. First of all, we need to distinguish between logical failure, which concerns the file system or partition, and physical failure, which concerns the hardware itself. Logical failure occurs when Windows can no longer read the partition table correctly, or when files are corrupted. In this case, the disk is usually visible in Disk Management or recovery software, and data can often be restored using specialized tools.
| Type of failure | Symptoms | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Logical failure | Disk recognized but inaccessible or empty | Use data recovery software. |
| Physical failure | Disk makes noise, vibrates or is not detected at all | Contact a specialized laboratory |
Before considering formatting or a complete reset, it’s important to try and save any data still accessible on the disk. Incorrect handling can worsen the condition of the medium and make recovery much more difficult, if not impossible. This precautionary step is essential if the disk contains irreplaceable personal or business files.
You can also find out how to recover data from the internal hard drive of an out-of-order PC.