Is your computer slow to start up, applications take forever to open, and even a simple copy of files seems to be a test of patience? Before blaming your processor or RAM, it may be time to evaluate the performance of your hard disk drive. AS SSD Benchmark is a tool designed to accurately measure the read and write speed of your storage. In this article, find out how to use it to find out if your drive is still up to scratch… or if it’s time to replace it.
Testing hard disk speed and wear under Windows (HDD, SSD and NVMe M.2.)
- AS SSD Benchmark: a tool designed to test the performance of SSD and HDD drives
- Install and configure AS SSD Benchmark to test your hard drive’s speed
- Compare results with manufacturers’ data
- Go further and test SSD wear and tear
- Go even further by analyzing every sector of the disk
- How can you optimize your hard drive to improve its lifespan?
AS SSD Benchmark: a tool designed to test the performance of SSD and HDD drives
AS SSD Benchmark is the essential reference software for measuring the speed of SSD and HDD drives under Windows. Developed specifically to evaluate SSD performance, it uses in-depth read and write tests to deliver reliable, reproducible results. Its simple interface, combined with detailed analysis of sequential and random speeds, makes it a popular tool for technicians and computer enthusiasts alike.
Unlike other generic benchmarks, AS SSD Benchmark simulates real-life usage scenarios to better reflect user-perceived performance. It offers several types of test:
- Sequential reading and writing: measures the transfer speed of large files, useful for assessing performance in mass storage.
- Random read/write (4K ): evaluates the disk’s ability to handle small writes, crucial for application and system loading times.
- Multithreaded test (4K-64Thrd): analyzes multitasking performance, using multiple input/output queues simultaneously.
- Access time: measures the time required for the disk to start reading or writing data, a key criterion for system responsiveness.
- Overall score: AS SSD Benchmark assigns a score that makes it easy to compare a drive’s performance with that of other models.
The tool features a copy test, which simulates the movement of real files, and a compression test, useful for analyzing the SSD controller’s handling of compressible and incompressible data.
Completely free and lightweight, AS SSD Benchmark is an ideal ally for anyone wishing to diagnose a drive, compare several models or ensure that their SSD is working to its full potential. It is particularly useful for detecting a drop in performance due to poor configuration, premature wear or the absence of optimizations such as TRIM.
Thanks to this tool, you can at last objectively measure the performance of your storage and check whether your SSD or HDD is living up to its promises.
Install and configure AS SSD Benchmark to test your hard drive’s speed
AS SSD Benchmark is freeware, and should be downloaded from a trusted source to avoid the risk of malware or modified versions. We recommend downloading AS SSD Benchmark directly from the official website of the publisher (Alex Intelligent Software).
One of the advantages of AS SSD Benchmark is that it requires no installation. After downloading the archive, simply open it to launch the software.
- Right-click on the ZIP file and select Extract all, or use software such as WinRAR or 7-Zip.
- You’ll get a folder containing the AS SSD Benchmark.exe executable.
No installation file is required.
- Simply double-click on AS SSD Benchmark.exe to launch the application.
AS SSD Benchmark automatically detects the drives installed on your PC.
Check that the correct disk is selected in the drop-down list at the top left of the interface.
By default, AS SSD Benchmark performs a full disk analysis, including sequential and random read and write tests.
For a quick test, you can limit the analysis by unchecking certain options, although this will reduce the accuracy of the results.
- Click on Start to begin the performance test.
Wait a few minutes: the tests may take some time, depending on the speed of your disk.
Once the benchmark is complete, AS SSD Benchmark will display drive performance in the form of MB/s speeds, access times and an overall score. Analysis of these results will enable you to assess whether your SSD or HDD is performing to its full potential.
How to interpret the AS SSD Benchmark results?
When you test a drive with AS SSD Benchmark, several values are displayed. Among them, three indicators are particularly important for assessing the overall performance of your storage: sequential read/write (Seq), access time (Acc.time) and overall disk score. Here’s how to understand and analyze them.
Sequential read/write speed (Seq)
Sequential read/write speed (Seq) refers to a disk’s ability to transfer large amounts of data continuously. It is particularly important for tasks involving large files, such as copying films, installing software or loading games. A conventional hard disk generally achieves a speed of between 80 and 160 MB/s, depending on its rotation speed and cache, while a SATA SSD can reach up to 600 MB/s.
If you use an external hard drive via USB, speed may be limited by the interface.
- An HDD connected via USB 2.0 will not exceed 40 MB/s, which considerably slows down transfers.
- With USB 3.0 or 3.1, an HDD will be able to exploit its full speed, but it will still be far inferior to an SSD.
- A USB 3.0 SATA SSD will offer similar performance to an internal SSD, as long as the interface is at least 5 Gbit/s.
- An NVMe SSD connected via USB 3.2 or Thunderbolt can reach several gigabytes per second, but only if the USB interface and controller are fast enough.
Access time (Acc.time)
Access time (Acc.time) or latency is the time it takes for the disk to start reading or writing data. It is measured in milliseconds and has a direct impact on system responsiveness.
- A conventional hard disk drive has an average access time of between 10 and 20 milliseconds, due to the mechanical displacement of the read head.
- Thanks to the absence of moving parts, a SATA SSD reduces this time to around 0.50 milliseconds, making it much faster to open files and programs.
- An NVMe SSD goes even lower, with values close to 0.05 milliseconds.
When a drive is used externally, the access time may be slightly longer due to the latency introduced by the USB interface, especially if the controller on the adapter or enclosure is of poor quality.
AS SSD Benchmark overall score
The overall drive score is a rating awarded by AS SSD Benchmark to give a quick overview of the storage medium’s overall performance. It is calculated from the results of the various tests and makes it easy to compare several models.
A conventional hard disk generally scores less than 300 points, a SATA SSD between 700 and 1,500 points, while a high-performance NVMe SSD can exceed 5,000 points. A USB-connected drive may see its score reduced if it is limited by the interface or a poor controller.
A significant drop in score compared with normal values may be a sign of hardware failure, incorrect settings or a connection problem.
Compare results with manufacturers’ data
When comparing the results of AS SSD Benchmark with the manufacturer’s specifications, it’s essential to assess whether the drive is still performing to its full potential, or whether it is beginning to show signs of wear.
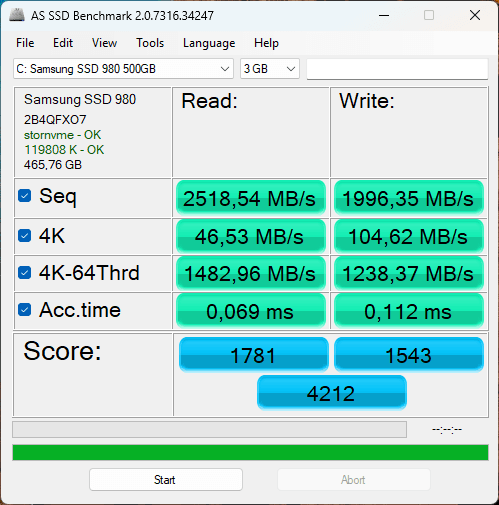
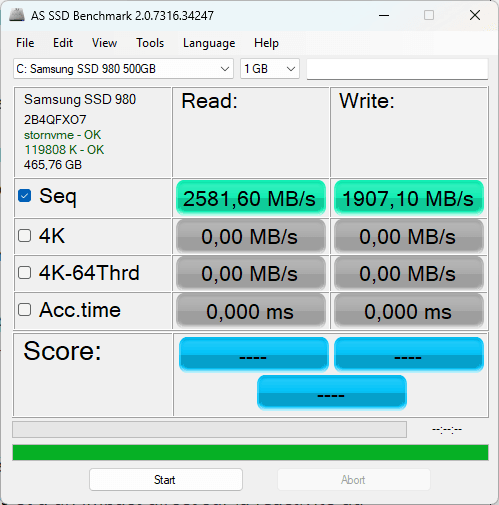
The Samsung SSD 980 is an NVMe PCIe 3.0 SSD which, according to official Samsung data, boasts theoretical sequential read and write speeds of up to 3,500 MB/s and 3,000 MB/s respectively.
However, in the benchmark results, measured speeds are 2,518 MB/s read and 1,996 MB/s write. This represents a significant drop of around 28% in reading and 33% in writing compared with the maximum performance advertised.
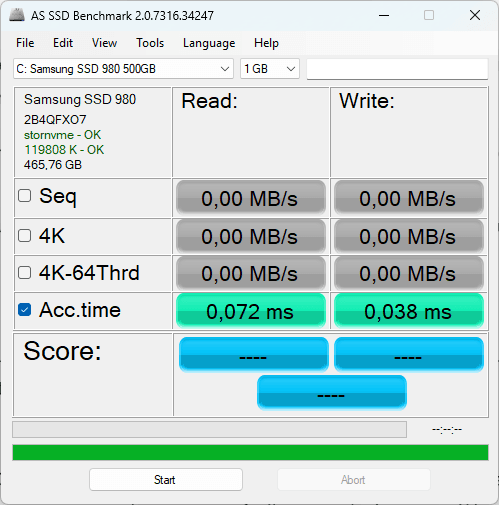
Access times remain within acceptable limits, however, at 0.069 ms for reads and 0.112 ms for writes, indicating that the SSD’s overall responsiveness is not yet totally degraded.
Finally, the overall score of 4,212 points is lower than that of a new Samsung 980, which typically hovers around 5,000 to 5,500 points in an AS SSD Benchmark test. This drop confirms that the SSD is no longer operating at full capacity.
These results suggest gradual wear and tear on the SSD, probably due to the high number of writes performed over time. It may be worth checking the condition of the SSD with software such as Samsung Magician to examine its percentage of wear and the volume of data written. If wear is advanced, a continuing drop in performance is to be expected, which may impact on overall system responsiveness.
Go further and test SSD wear and tear
To go a step further in analyzing the performance and health of an SSD, we’ll be using diagnostic software such as CrystalDiskInfo. This provides access to S.M.A.R.T. data, giving precise information on wear and tear, number of operating hours and volume of data written.
After installing and running CrystalDiskInfo, we obtain a health status of 93%, suggesting that the SSD is slightly worn but still in good condition overall. However, cross-referencing this data with the performance readings from AS SSD Benchmark, it appears that the drive has undergone more significant degradation than might appear.
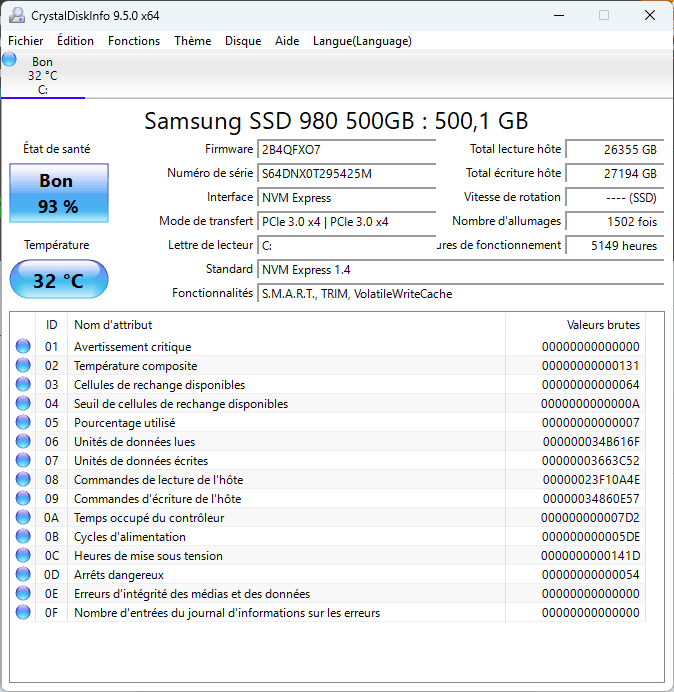
The SSD displays a total of 27,194 GB written, which remains reasonable for a 500 GB drive. Nevertheless, the performance measured in AS SSD Benchmark shows a noticeable drop in comparison with the values of a new SSD, particularly in writing, where there’s a loss of around 33%. This may indicate that, although the SSD retains good endurance, its NAND cells are beginning to lose efficiency, leading to a reduction in throughput.
If this trend continues, the SSD is likely to lose even more speed in the coming months. To prolong its lifespan, it may be useful to check that TRIM is enabled, and to avoid filling the drive to more than 70% of its capacity.
Go even further by analyzing every sector of the disk
When performance tests show a drop in speed or potential wear and tear on an SSD, it’s important to go a step further by analyzing every sector of the drive. This approach detects degraded NAND blocks, slow sectors or unrecoverable errors that could lead to progressive performance deterioration and data loss.
The HDDScan tool is ideal for this type of in-depth analysis, thanks to its read test which evaluates the SSD’s ability to read and verify the integrity of stored data. This step-by-step tutorial will guide you through how to perform this check on your SSD.
HDDScan is a free, portable software package that requires no installation. You can download it from its official website.
After downloading the archive, simply extract it and run the HDDScan.exe file.
Open HDDScan and select your NVMe SSD or other drive from the list of detected drives.
Click on the Tests button and choose Verify (read-only test).
Start the test and wait while HDDScan scans each sector.
In our case, all the blocks analyzed were in perfect condition, all (or almost all) responding in less than 5 ms. No slow, unstable or damaged sectors were detected, indicating that the SSD is operating correctly.
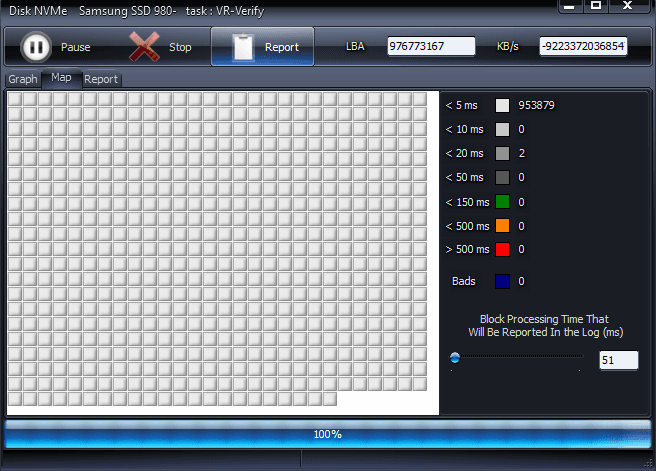
These results come as a pleasant surprise, because despite a drop in performance observed in AS SSD Benchmark, sector-by-sector analysis shows that there is no notable physical deterioration of the SSD.
The best disk wear analysis tools
Samsung also offers its own optimization and diagnostic software, Samsung Magician, which can analyze an SSD sector by sector to detect possible read errors or faulty blocks. This tool offers a complete solution for monitoring drive status, optimizing performance and applying firmware updates specific to Samsung models. The analysis performed by Samsung Magician is particularly useful for checking the reliability of NAND cells and ensuring that the SSD operates without critical errors.
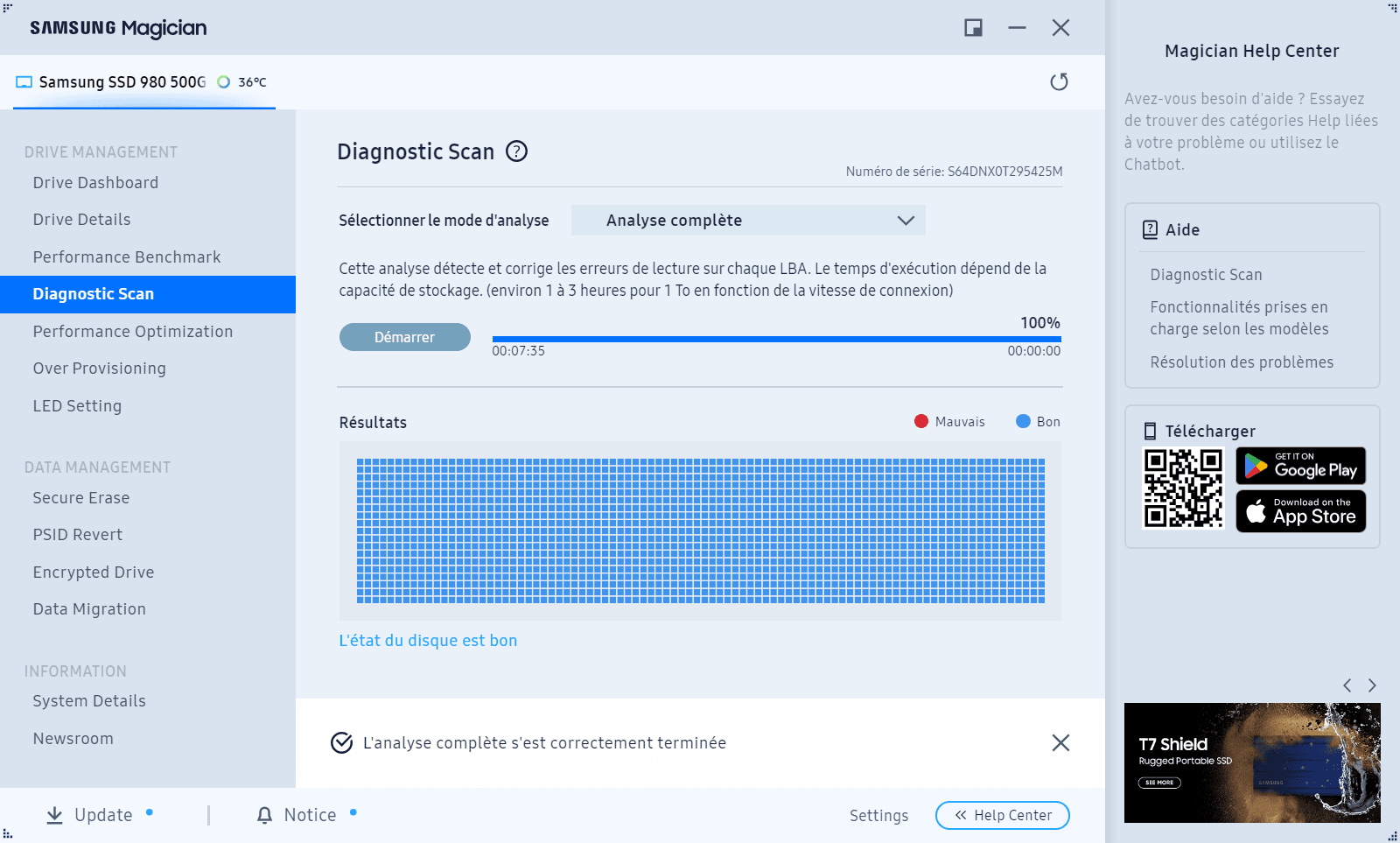
However, this solution is exclusively reserved for Samsung SSDs, limiting it to users who own these models. For a more universal approach, HDDScan remains the best alternative, as it works with all drive types, whether SATA/NVMe SSDs, mechanical hard drives (HDDs) or even USB sticks and external hard drives. Its advanced surface test enables precise diagnosis of any storage medium, regardless of manufacturer.
Other manufacturers like Crucial also offer their own SSD management software, Crucial Storage Executive, which includes features similar to those of Samsung Magician, including SMART optimization and monitoring tools.
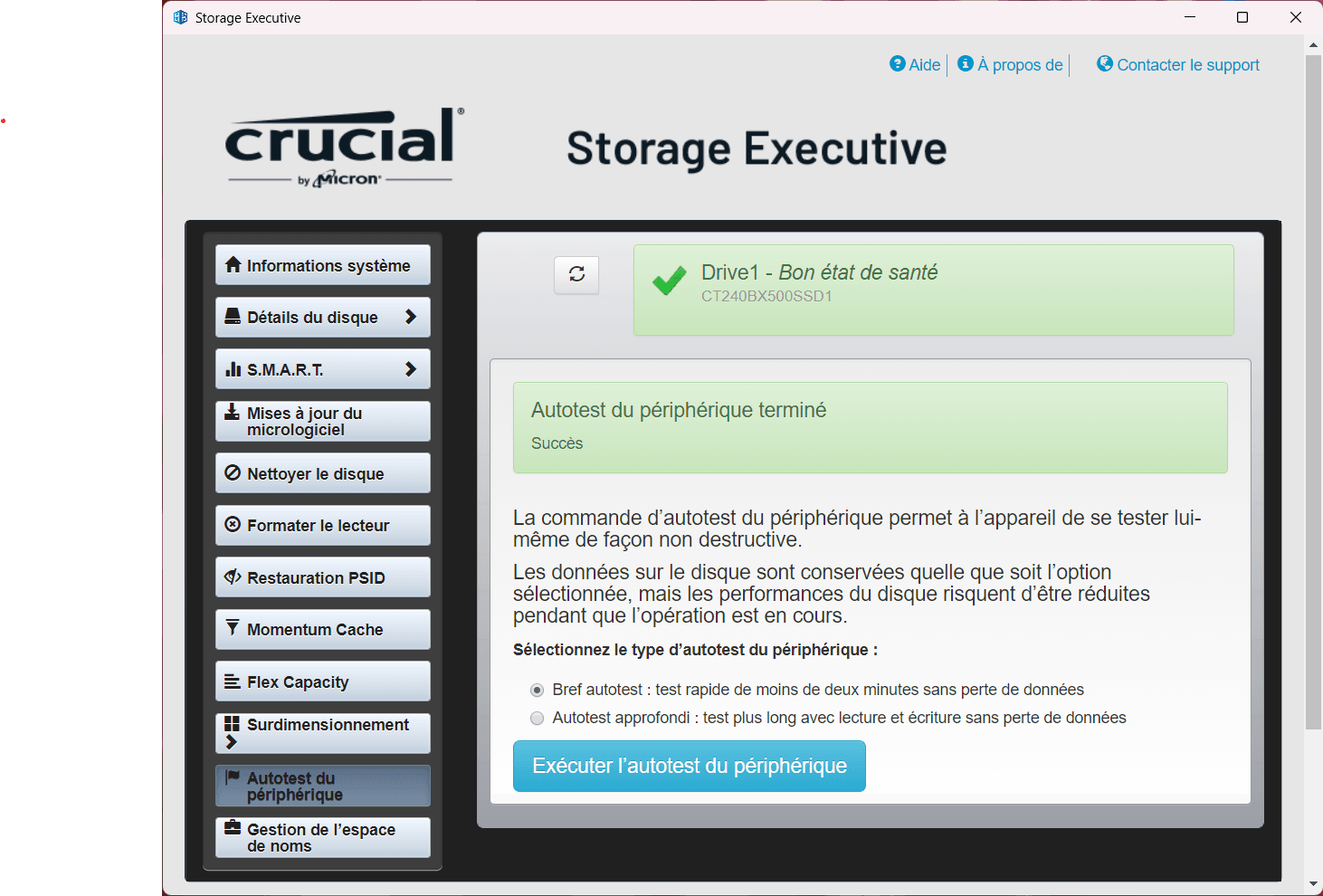
However, as with Samsung, this software is designed exclusively for the brand’s SSDs.
How can you optimize your hard drive to improve its lifespan?
Optimizing a hard disk drive is essential to maintain its performance and extend its lifespan. Whether you’re using a mechanical HDD or an SSD, maintenance methods differ, as the two technologies work in very different ways.
- An HDD (conventional hard disk drive) relies on magnetic platters and a mechanical read head. Its main problem is file fragmentation, which slows down data access and increases mechanical wear and tear.
- An SSD (Solid State Drive) stores data in electronic cells and does not suffer from fragmentation. However, it does have a write cycle limit, which requires specific management to avoid premature wear and tear.
HDD optimization: defragmentation
Over time, files stored on a hard disk can become fragmented, i.e. split into several pieces in different places on the disk. This slows down performance, as the read head has to traverse several zones before accessing a complete file.
To optimize an HDD under Windows :
- Open the defragmentation tool by typing Defragment and optimize drives in the Windows search bar.
- Select your HDD from the list.
- Click on Optimize to start defragmenting.
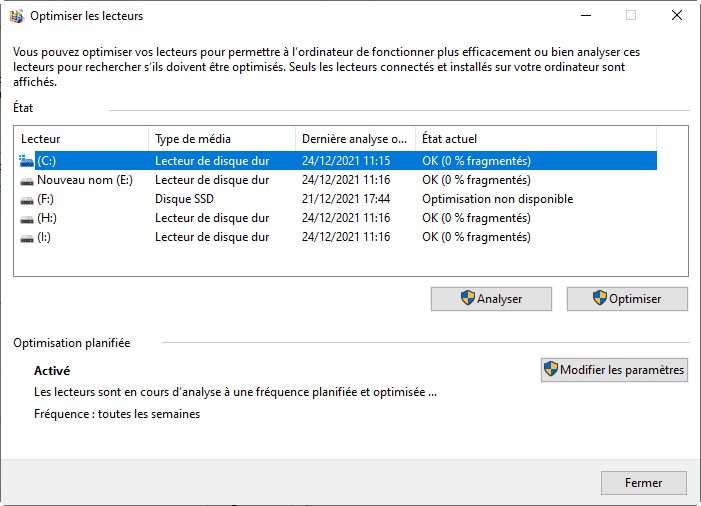
It is recommended to perform this operation once a month on a conventional hard disk to maintain optimum performance.
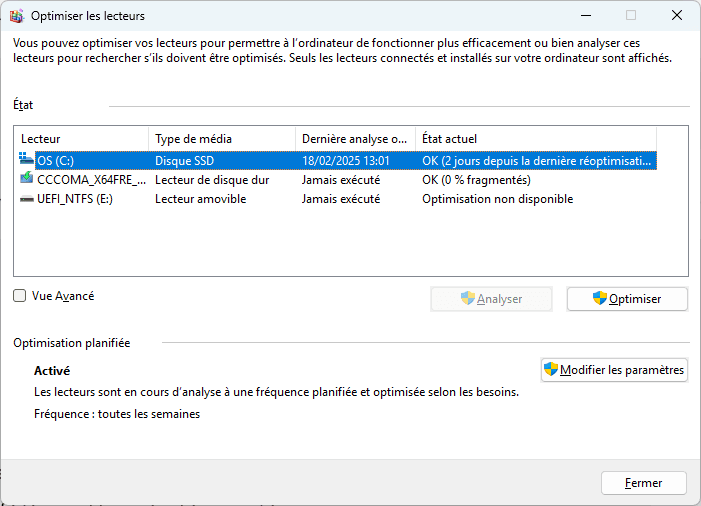
Optimizing an SSD: activate and check TRIM
Unlike HDDs, SSDs should never be defragmented, as this would lead to unnecessary writes and accelerate the wear and tear of memory cells. Instead, Windows manages the erasure of unused blocks with the TRIM command, which enables the SSD to erase unnecessary cells in the background to speed up future writes.
To check whether TRIM is enabled on Windows :
- Open the command prompt (type
cmdand run in administrator mode). - Type the following command and press Enter:
fsutil behavior query DisableDeleteNotify- If the answer is 0, TRIM is activated and works correctly. If the answer is 1, it is deactivated and must be activated with this command :s
fsutil behavior set DisableDeleteNotify 0Windows automatically runs SSD optimization via its built-in maintenance tool :
- Type Defragment and optimize drives in the Windows search bar.
- Select your SSD and click on Optimize.
- Windows will then send the TRIM command to the SSD to free unused blocks.
Other tips for extending the life of your drive
Keep your drive at a reasonable temperature: HDDs should be kept below 50°C, SSDs below 70°C, to avoid premature wear.
Avoid filling your disk to more than 80%: free space is needed for the disk to manage files and background operations efficiently.
Now you know everything you need to know to fully test a hard drive
Thanks to the various methods we’ve explored, you now have all the keys you need to carry out an in-depth analysis of your disk’s performance and state of health.
From checking read and write speeds with AS SSD Benchmark, to S.M.A.R.T. and wear cycle analysis with CrystalDiskInfo, to sector-by-sector testing with HDDScan, each step gives you a complete picture of the real state of your storage.
You’ve also seen that you shouldn’t always rely blindly on manufacturers’ figures, as actual performance can vary according to many parameters: NAND cell wear, disk filling, SLC cache management and connection interface limitations.