Every time Windows starts up, it launches a multitude of background services to keep the system running smoothly. Some are indispensable, others much less so. Yet these invisible processes consume memory, processor resources and bandwidth. In the long run, they can slow down your computer, lengthen start-up times and impair the overall fluidity of Windows. It’s possible to regain control by deactivating services you don’t need, and considerably lighten the system’s load without compromising its stability. This guide shows you how to identify unnecessary services, understand their role and optimize Windows to make it as responsive as possible.
Why does Windows run services in the background?
Windows is first and foremost a universal operating system , designed to run on millions of different configurations and meet every need: home users, professionals, gamers, businesses, schools and government agencies. To offer this turnkey compatibility, Microsoft integrates a large number of background services by default, ready to run when needed.
A Windows service is a background, silent, stand-alone program that runs as soon as the system starts up and remains active to perform a specific function, such as Windows Update, which manages updates, Bluetooth Support Service, which maintains the connection with your wireless devices, Windows Search, which indexes your files to speed up searches, or the Print Spooler, which manages the print queue.
These services have an impact on performance. Each one consumes a share of RAM, puts a strain on the processor and can even reduce battery life on a laptop. When too many services are running simultaneously, the system loads unnecessarily and loses resources that could be used for other purposes.
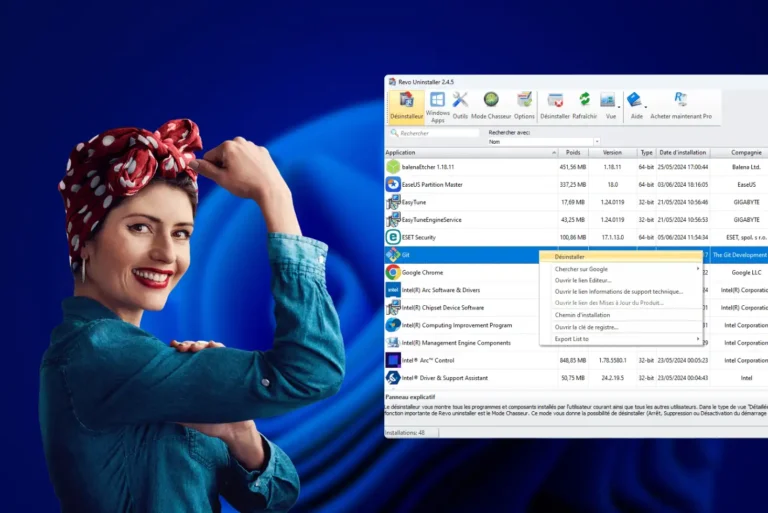
Disable unnecessary services via the services console
The Windows operating system embeds a large number of internal services. Some are essential to system stability, while others are only useful in specific contexts (remote connection, printing, sensors, etc.). By manually disabling services you don’t need, you can speed up Windows startup, free up RAM and improve overall PC responsiveness without compromising its smooth operation.
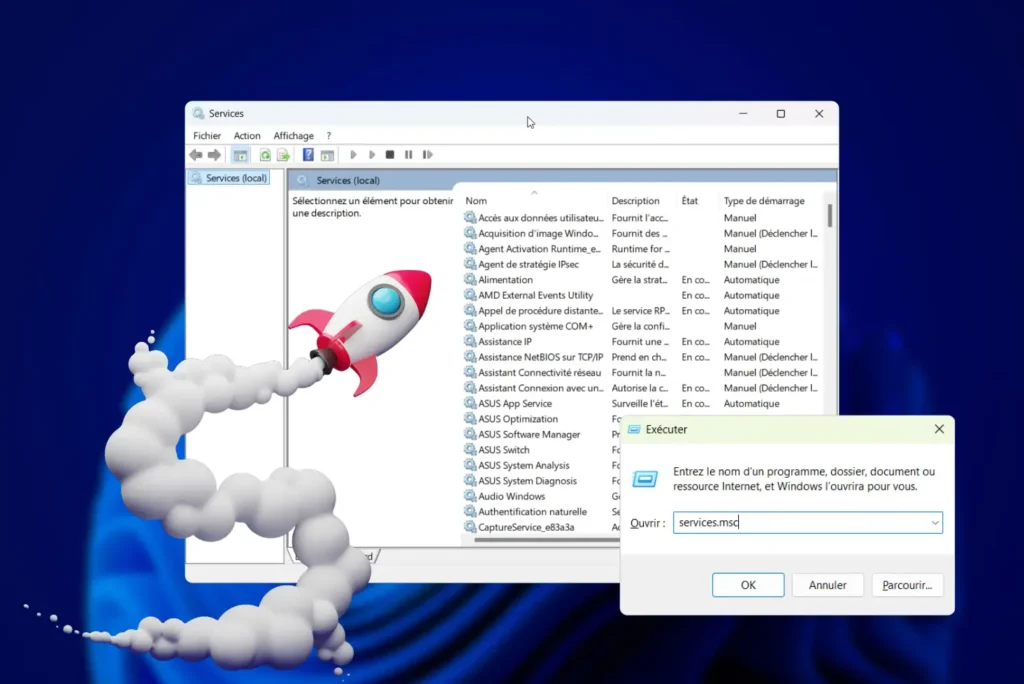
- Press Windows + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Then type services.msc and click OK.
Windows then opens the Services console, an administration interface that lists all the services active or available on your computer.
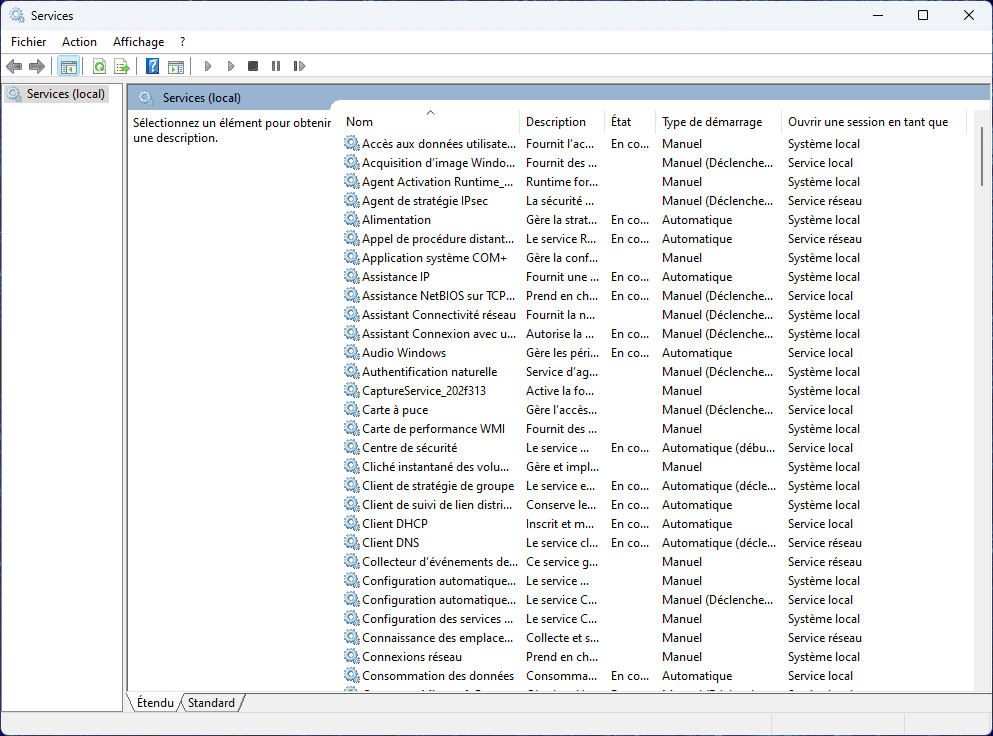
Before disabling anything, it is important to understand the three possible modes:
- Automatic: the service starts every time Windows is launched.
- Manual: the service runs only when an application requires it.
- Deactivated: the service remains inactive until you reactivate it.
- Double-click on one of the services you wish to disable, then under Startup type, select Disabled.
You can also select Manual if you prefer the service to start only when an application requires it.
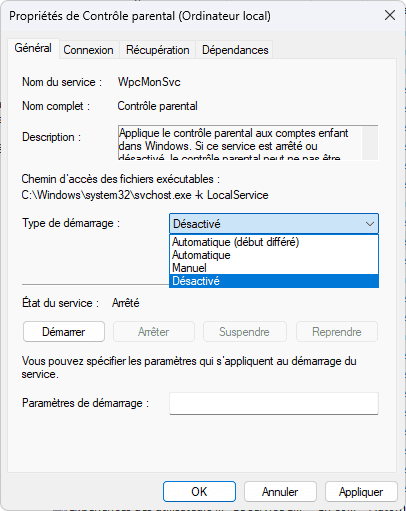
Click Apply, then OK. The service will be deactivated the next time the system is restarted.
Once you’ve completed this step, you can continue with the list of Windows services that can be disabled below.
And to take things a step further, find out how to uninstall bloatware and unnecessary applications preinstalled on Windows 11.
List of unnecessary services to disable to speed up your PC
Not all Windows services are equally important. Some provide vital functions, while others are used only occasionally or for very specific purposes. If your aim is to lighten the system without altering its stability, start with personal-use services, which are not essential to the basic operation of Windows and can be safely deactivated to suit your needs. These services are mainly related to local search, data collection or cloud and test functions that most users never use.
Disable Windows services for personal use
| Department name | Main role | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Windows Search | Indexes files to speed up searching | Disable if you don’t search for files often |
| Optimize delivery | Share Windows updates over the network | Disable if only one PC or fast connection |
| Connected user experience and telemetry | Sends statistics to Microsoft | Disable for greater confidentiality |
| Windows Error Reporting Service | Sends error reports online | Disable if not needed |
| Work Folders | Synchronizes files on a corporate server | Disable on home PC |
| Windows Insider Service | Manages Windows Insider Program updates. | Disable on stable versions |
Services for seldom-used features
Some Windows services are designed to meet the very specific needs of professional environments, rare peripherals or technologies not widely used by the majority of users. On a personal computer, these services run uselessly in the background, consuming memory without any real benefit. By disabling them, you can lighten Windows without compromising its essential functions.
Here are the main services you can safely disable if you don’t use these features:
| Department name | Main role | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Smart card | Smart card authentication and locking | Disable on home PC |
| Telephony | Call management from PC | Disable unless using Phone Link |
| Windows biometrics service | Biometric sensor management (fingerprint, face) | Disable if no sensor |
| Sensor service | Sensor management (GPS, light, motion) | Disable on fixed PC |
| Geolocation service | Provides geographical position of device | Disable if no GPS or privacy concerns |
| Bluetooth support service | Communication with Bluetooth devices | Disable on PC without Bluetooth or not in use |
Other Windows services to disable depending on your usage
Apart from purely personal or sensor-related services, Windows also integrates numerous modules for security, remote connection, gaming and peripheral management. These are useful in certain situations, but can be safely deactivated when not in use. This selection will help you fine-tune system performance even further.
| Department name | Main role | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| BitLocker drive encryption service | Encrypts disks to protect data | Disable if BitLocker is not used |
| Remote Desktop Service | Allows access to the PC from another device | Disable if not used |
| Xbox Services | Authentication, backup and management of Xbox accessories | Disable if not playing |
| Print spooler | Manages local and network printing | Disable if no printer |
| Parental control | Manage access restrictions for children’s accounts | Disable on home PC |
If you notice any problems after disabling a service, you can always easily re-enable it in the same way via the Services Console.
What are all the Windows services for?
| Service name | Description | Criticality |
|---|---|---|
| RPC (Remote Procedure Call) | Essential for inter-process communication and overall Windows stability. | Critical |
| DCOM Server Process Launcher | Launches DCOM servers to run distributed applications. | Critical |
| RPC Endpoint Mapper | Manages access requests to RPC services. | Critical |
| Plug and Play | Ensures automatic device detection and configuration. | Critical |
| Windows Firewall / Windows Defender Firewall Service | Protects the system against unauthorized access and external threats. | Critical |
| Windows Update | Manages system updates. Keep for security or manage manually. | Depends on use |
| Windows Defender | Provides native antivirus protection. Disable only if another solution is installed. | Usage-dependent |
| Task Scheduler | Automatically executes scheduled tasks and system operations. | Critical |
| DHCP Client | Dynamically assigns IP addresses required for network connection. | Critical |
| DNS Client | Resolves domain names into IP addresses for Internet browsing. | Critical |
| Network Location Awareness | Determines network location to apply appropriate security policies. | Critical |
| Network List Service | Provides information on connected networks. | Critical |
| Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) | Provides information and events for system management and monitoring. | Critical |
| Windows Event Log | Records system events for logging and troubleshooting. | Critical |
| COM+ Event System | Supports event communication between COM+ applications. | Critical |
| Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS) | Handles background data transfers, especially for Windows Update. | Depends on usage |
| Print Spooler | Manages the print queue. Can be deactivated if no printer is in use. | Can be disabled |
| Windows Search | Indexes files to speed up searches. Can be disabled if not in use. | Can be disabled |
| Superfetch (SysMain) | Optimizes performance by preloading frequently used applications. | Depends on usage |
| Bluetooth Support Service | Manages communication with Bluetooth devices. | Usage-dependent |
| Windows Audio | Manages system audio playback. | Usage-dependent |
| Windows Audio Endpoint Builder | Manages audio devices. | Usage-dependent |
| Windows Installer | Supports software installation, maintenance and uninstallation. | Critical |
| Application Experience | Helps ensure compatibility of older applications with newer versions of Windows. | Depends on use |
| Windows Error Reporting Service | Collects and sends error reports to Microsoft to improve the system. | Usage-dependent |
| Windows Event Collector | Collects events from other machines on the network. | Depends on usage |
| Windows Time | Synchronizes system time with a time server. | Critical |
| IP Helper | Supports IPv6 protocols and virtual networks. | Critical |
| Windows Process Activation Service | Manages process activation for web applications and other services. | Critical |
| Windows Image Acquisition (WIA) | Manages image acquisition from scanners or cameras. | Depends on usage. |
| Cryptographic Services | Manages encryption and certificate security. | Critical |
| Certificate Propagation | Facilitates the communication of certificates between devices. | Usage-dependent |
| Distributed Link Tracking Client | Maintains links to shortcuts and files on the network. | Critical |
| Function Discovery Provider Host | Facilitates detection and publication of network resources. | Critical |
| Function Discovery Resource Publication | Publishes network resources for easy discovery by other devices. | Critical |
| Human Interface Device Service | Manages interface devices (keyboards, mice, etc.). | Usage-dependent |
| AppX Deployment Service (AppXSVC) | Manages the deployment and updating of Windows Store applications. | Usage-dependent |
| Program Compatibility Assistant Service | Helps resolve compatibility problems with older applications. | Usage-dependent |
| Smart Card | Manages smart card devices for authentication. | Usage-dependent |
| Smart Card Removal Policy | Manages secure disconnection of smart cards. | Usage-dependent |
| Windows Update Medic Service | Helps maintain and repair the Windows Update service. | Usage-dependent |
| Windows Store Service | Manages access and downloads from the Microsoft Store. | Usage-dependent |
| WSDPrint (WSD-Print Service) | Manages printing to WSD-compatible printers. | Can be disabled |
| Windows Backup | Supports system backup and restore. | Depends on use |
| Windows Biometric Service | Manages biometric devices (fingerprints, facial recognition). | Usage-dependent |
| Windows Camera Frame Server | Manages access to cameras and video streams. | Usage-dependent |
| Windows Connect Now | Facilitates rapid configuration of wireless connections. | Usage-dependent |
| Windows Remote Management (WinRM) | Enables remote management of Windows via WS-Management. | Usage-dependent |
| Windows Insider Service | Manages updates and returns from the Windows Insider program. | Usage-dependent |
| Windows Location Provider | Provides location information for certain applications. | Usage-dependent |
| Windows Remote Desktop Services | Manages remote desktop connections. | Usage-dependent |
| Network Connectivity Assistant | Helps with network connectivity and troubleshooting. | Critical |
| Security Center | Monitors system security status (antivirus, firewall, updates, etc.). | Depends on usage |