There’s an astronomical amount of malware out there, the best-known being viruses thanks to their biological counterparts (the flu virus, for example). The term virus is often used to refer to malware, although the real name for this large family is malware. In this article, I’m going to tell you about the different categories of malware and how to protect yourself against them.
Your knowledge of computer viruses needs updating
Most people think that viruses are the big family of malware. This idea is incorrect. In fact, the proper term for all malicious software is malware, short for malicious software. Malware comprises a number of different categories, of which viruses are just one.

Malware also includes other types of malicious software such as Trojans, worms, ransomware and spyware, to name but a few. Each type of malware has its own characteristics and modus operandi. Viruses, for example, are programs that replicate themselves by infecting other executable files, but they represent only a small part of the malware ecosystem.
What are the main types of malware and how can you protect yourself?
Explore the main types of malware, from the virus family to the dreaded ransomware. We’ll look at their characteristics, how they work and the telltale signs of infection, giving you the tools you need to recognize and protect yourself against these threats.
Computer viruses: Preventing and eliminating threats to your system
Viruses are malicious programs designed to spread by infecting other files or programs on your computer. Once infected, a virus can damage your files, corrupt your operating system or even steal your personal data. Viruses are usually transmitted via file downloads or infected e-mail attachments.

How do viruses work?
- Propagation via executable files or scripts.
- The virus attaches itself to files or the system’s boot table to run each time the computer starts up.
- It can corrupt or delete files, steal data or even take complete control of the system.
How can I protect myself from viruses?
- Use reliable antivirus software and keep it up to date to regularly scan your system for viruses.
- Avoid downloading software from unreliable sources, and be sure to check downloaded files before opening them.
- Keep your operating system and applications up-to-date with the latest security patches to plug vulnerabilities exploited by viruses.
Computer worms: How to detect them and eliminate them from your network?
Worms are a type of malware that spread automatically across computer networks by exploiting system vulnerabilities. Unlike viruses, worms don’t need to be attached to files to spread, which often makes them more dangerous and harder to contain. They can infect a large number of computers in a short space of time, compromising network and data security.
How do worms work?
- Exploits security holes to automatically spread to other computers connected to the same network.
- Once a computer is infected, the worm actively seeks out other devices to infect.
- Can run in the background without any user interaction.
How can I protect myself from worms?
- Install a robust firewall to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic.
- Implement network security rules to limit unauthorized access to your systems.
- Apply regular security patches to software, applications and the operating system to correct vulnerabilities that can be exploited by worms.
Computer Trojans: How to minimize the risks?
Trojans are malware programs that present themselves as legitimate programs or useful files, but actually contain hidden malicious functionality. Once installed on your computer, a Trojan can open a backdoor, allowing cybercriminals to gain remote access to your system, steal sensitive data or cause other damage.

How do trojans work?
- Masquerades as legitimate software to trick users into installing it.
- Once installed, the Trojan can open a backdoor on the system, allowing attackers to access sensitive data or control the computer remotely.
- Trojans can be used to steal information, spy on users or cause damage to systems.
How can I protect myself from Trojans?
- Be careful when downloading and installing software, and avoid unreliable sources.
- Use antivirus software that offers real-time protection against Trojans and other malware.
- Don’t click on suspicious links or attachments from unknown senders in e-mails.
Spyware: signs of infection and tips to protect your privacy
Spyware is designed to secretly collect information about your online and offline activities, such as browsing habits, passwords, financial information and so on. This information is then often used for malicious purposes, such as identity theft or intrusive ad targeting. Spyware is often installed without your knowledge by downloading malware or visiting compromised websites.

How does spyware work?
- Often installed discreetly with legitimate software or via malicious downloads.
- Monitors user activities, collecting personal information such as passwords, credit card numbers, browsing history, etc.
- Transmits collected data to third parties for malicious activities such as identity theft or intrusive advertising targeting.
How can I protect myself from spyware?
- Use anti-spyware software to detect and remove spyware from your system.
- Avoid downloading software from unsecured websites, and read license agreements carefully before installing software.
- Keep your browsers and extensions up to date, and use ad blockers to reduce the risk of spyware infection.
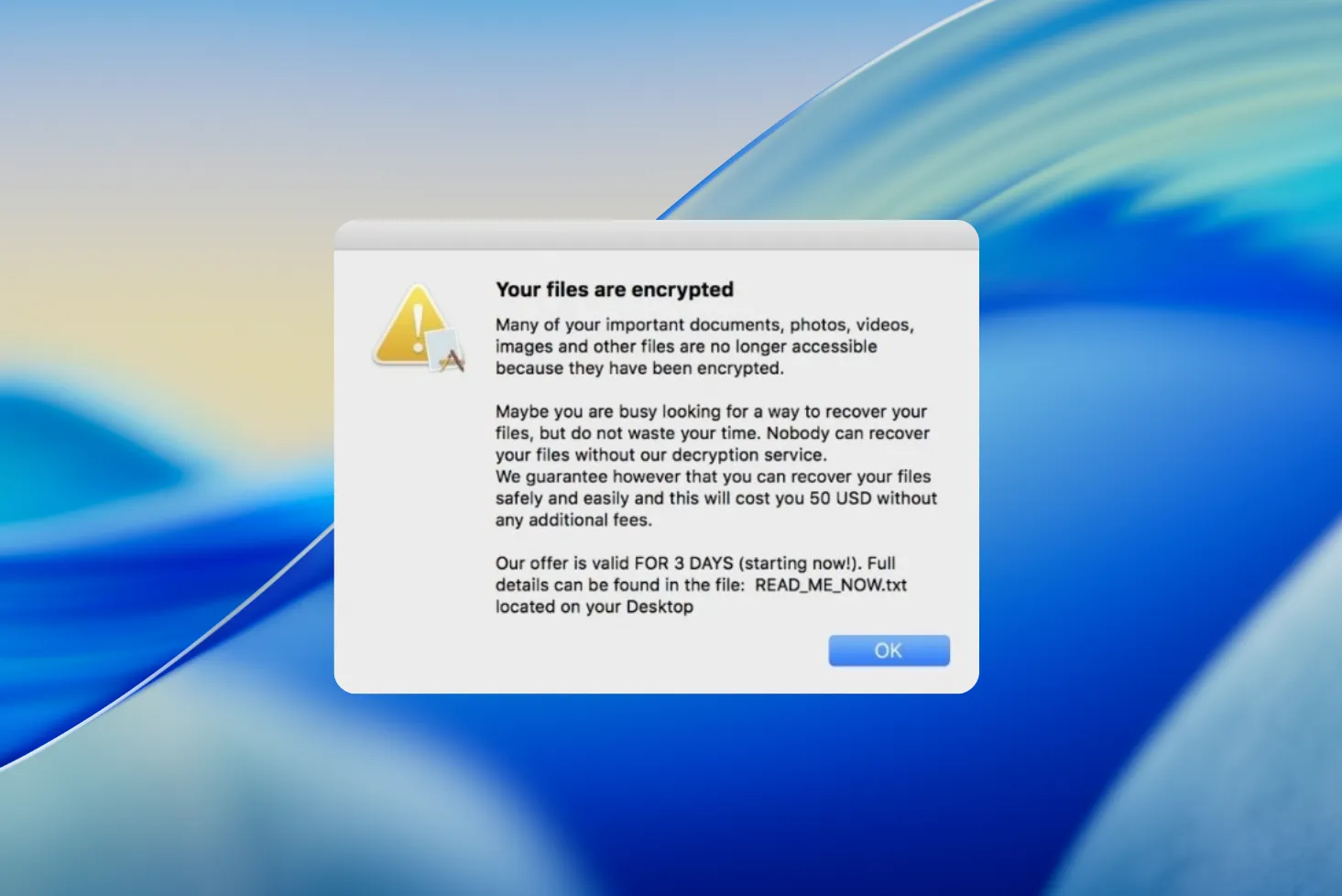
Ransomware: Protect your data against online threats
Ransomware is malicious software that encrypts your files and demands payment of a ransom to decrypt them. Once infected, you may find yourself unable to access your personal files, photos, documents, etc. Ransomware is often distributed via e-mail attachments or pirated software downloads, and can cause significant damage to your data and privacy.

How does ransomware work?
- Encrypts user files using a strong cryptographic algorithm.
- Displays a ransom message demanding payment in exchange for the decryption key.
- Can spread via malicious attachments, compromised websites or system vulnerabilities.
How to protect yourself against ransomware?
- Back up your important data regularly on external storage media or in the cloud.
- Use antivirus software that offers protection against ransomware and detection of suspicious behavior.
- Avoid clicking on suspicious links or attachments in e-mails, and make sure your e-mail software filters out spam and malicious e-mails.
Adware: signs of infection and measures to block intrusive ads
Adware is a program that displays unsolicited advertising on your computer, often in the form of annoying pop-ups or browser redirects. These ads can interfere with your browsing experience and slow down your computer’s performance. Adware is usually installed without your knowledge by downloading freeware or visiting malicious websites.
How does adware work?
- Often comes with freeware or suspicious downloads.
- Displays intrusive advertising in the form of pop-ups, banners or browser redirects.
- Generates revenue for malware developers by clicking on ads or redirecting users to fraudulent websites.
How to protect yourself from adware?
- Avoid downloading software from unverified sources, and carefully read the notices and conditions of use before installing any software.
- Use ad blockers in your browser to reduce the risk of malicious ads being displayed.
- Regularly update your software and applications to correct vulnerabilities exploited by adware.
Rootkits: Securing your system against this malware
Rootkits are malware packages designed to hide the presence of other malware on your system by modifying its functions so that they are difficult to detect and remove. Rootkits are often used by cybercriminals to maintain unauthorized access to a compromised system and to hide other malicious activities, such as data theft or sabotage.

How do rootkits work?
- Modifies system components to mask its presence and prevent detection by security software.
- Integrates deeply into the operating system, making it difficult to remove.
- Can be used to install other malware or to grant persistent access to an attacker on the infected system.
How can I protect myself from rootkits?
- Use rootkit detection tools to regularly scan your system for hidden malware.
- Restrict administrative privileges on your system to limit the installation of unauthorized software.
- Monitor suspicious activity on your network and system, such as unauthorized modifications to system files or suspicious outgoing connections.