Has your computer charger decided to give up on you, and you’re not sure whether to repair it or buy a new one? Rest assured, you’re not alone! Chargers can fail for a variety of reasons: damaged cables, worn connectors or faulty internal components. But the good news is that, in many cases, repairs are possible. So, before you spend your money or throw your charger in the garbage can, let’s see if a second life is possible for this indispensable accessory.
Broken computer charger: is it possible to repair it?
- What causes a dysfunctional charger?
- Unable to repair your charger?
- Is your charger detachable? Replacing a damaged charger cable
- What’s the difference between IEC C5 (cloverleaf) and IEC C13 (cold plug) cables?
What causes a dysfunctional charger?
A charger that no longer works is a frustrating situation that many of us have already experienced. Whether for a smartphone, laptop or tablet, a faulty charger can quickly disrupt our habits. But what are the causes? Here’s an overview of the main factors behind a dysfunctional charger.
A damaged power cable
Power cables for PC chargers are often put to the test: twisting, pinching or natural wear and tear. This can lead to internal cuts that prevent electricity from flowing properly. Common symptoms are :
- The charger only works if the cable is positioned in a certain way.
- Torn or burned areas are visible on the cable.
Solution: If the cable is detachable, replace it with a compatible model. Otherwise, consider replacing the entire charger.
Problem with connector (ferrule)
The connector that plugs into the PC is a weak point. Over time, it can become damaged, bent or collect dust. If the connector doesn’t make good contact with the computer’s charging port, the current won’t flow. Common symptoms are :
- The PC only charges when you move the tip slightly.
- The connector seems loose in the charging port.
Solution: Clean the port gently (a toothpick or compressed-air canister can help). If the problem persists, replace the charger or have the charging port repaired.
Non-compatible or poor-quality charger
If you use a generic or uncertified charger, it may not provide the voltage or current required for your laptop. Poor-quality chargers can also fail more quickly.
Solution: Always use an official or certified charger for your PC model. Check the technical specifications (voltage and amperage) on the adapter label before purchase.
Overheating or overload
Prolonged use, poor ventilation or overloading can damage the power supply unit. Some chargers trip in the event of overheating, but this can also indicate an internal fault. Common symptoms are :
- The charger becomes abnormally hot to the touch.
- A burning smell or unusual noises (buzzing) are perceptible.
Solution: Let the charger cool down before using it again. If the problem persists, replace the charger.
Wall socket or power strip failure
Sometimes the problem is not with the charger, but with the wall socket or power strip you’re using. A faulty outlet may cause intermittent power cuts or fail to supply sufficient electricity.
Symptoms :
- The charger works on another plug, but not on the one normally used.
Solution: Test another plug and make sure your power strip is in good condition.
PC problem
If the charger is in good condition but the PC won’t charge, the problem may lie with the charging port or the computer battery. The port may be damaged, or the battery completely out of order.
Symptoms :
- The PC switches off immediately when the charger is disconnected.
- Charging port appears loose or damaged.
Solution: Have your computer repaired by a professional to diagnose and replace the faulty parts.
Unable to repair your charger?
Despite your best efforts, your charger may be beyond repair. Rather than risk damaging your equipment with an unsuitable charger, discover our buying guide to choosing the right universal charger. You’ll find advice on how to find the model that’s perfectly compatible with your laptop.
Is your charger detachable? Replacing a damaged charger cable
Have you noticed that your laptop or computer charger is no longer working properly? If the problem is with the power cable, the good news is that it can often be replaced without having to change the whole charger. With standard cables such as the IEC C5 (Cloverleaf) connector or the IEC C13 (Cold plug) connector, you can have a fully functional charger back in no time.
Buy an IEC C13 connector (cold plug)
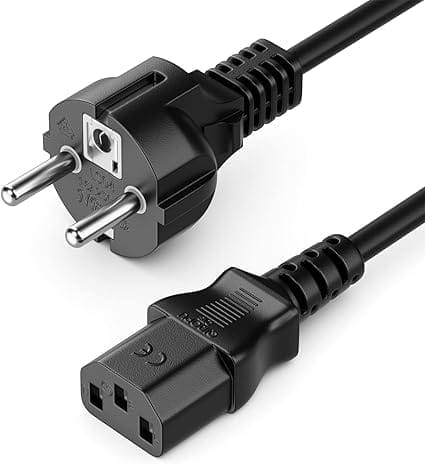

Editor's Verdict :
Le cable IEC C13 sera parfait pour réparer votre chargeur cassé, attention toutefois à la longueur du câble.
Buy at the Best Price on Amazon
Buy an IEC C5 connector (Cloverleaf)
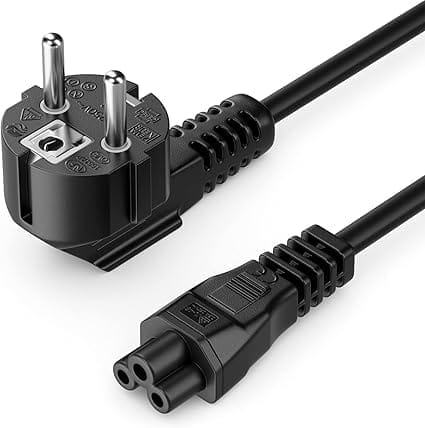

Editor's Verdict :
Le cable IEC C5 (Trèfle) sera parfait pour réparer votre chargeur cassé, attention toutefois à la longueur du câble.
Buy at the Best Price on Amazon
What’s the difference between IEC C5 (cloverleaf) and IEC C13 (cold plug) cables?
When looking to replace or purchase a power cable, it’s essential to choose the right type of connector. Among the most common are IEC C5 (cloverleaf) and IEC C13 (cold plug) cables. These two types of cable are often confused, but their uses, design and capacities differ considerably.
| Criteria | IEC C5 (Cloverleaf) | IEC C13 (Cold plug) |
|---|---|---|
| Supported power | Up to 250W | Up to 2500W |
| Powered devices | Laptops, consoles | Stationary PCs, monitors |
| Cable quality | Light, thinner | Robust, often shielded |
| Size and transport | Compact, easy to carry | More bulky |
| Average price | Less expensive | More expensive |
| Connector | Cloverleaf | Rectangular with three pins |
| Applications | Domestic use | Professional use |
| Safety | For low-power devices | For energy-hungry devices |