Batch files (.bat), which first appeared with the first versions of MS-DOS, are one of the oldest ways of automating tasks under Windows. Even today, they are still widely used for repetitive actions, systems management and software deployment. Thanks to their simplicity and compatibility with almost all versions of Windows, they are an indispensable tool for administrators and advanced users alike. In this article, we’ll explore how to create and run a batch file, as well as some basic commands to get you started.
How do I create a batch file (.bat or .cmd) under Windows?
- What is a Batch file?
- Tutorial: Creating a batch file in Windows
- Batch file example and use case
- The main Batch commands for Windows
- The limits and evolution of scripting under Windows
What is a Batch file?
A Batch file (or Batch script) is a text file containing a series of commands executed sequentially by the Windows command interpreter (cmd.exe). These files are mainly used to automate repetitive tasks without manual intervention.
Historically introduced under MS-DOS, Batch files are still a simple way of executing system instructions, despite the emergence of more modern languages such as PowerShell. They are particularly appreciated for their lightness and compatibility with all versions of Windows.
The main purpose of a batch file is to automate operations such as :
- Execute multiple commands in a single action,
- File and folder management (create, delete, copy),
- System administration (shutdown/restart, process management),
- Automatic software launch,
- Installing or configuring programs on multiple machines.
Tutorial: Creating a batch file in Windows
Batch files allow you to automatically execute a series of commands in Windows. They are particularly useful for automating common tasks such as displaying messages, managing files or launching programs. In this tutorial, we’ll look at how to create a batch file and execute it, with a simple example using the echo command.
A batch file is simply a text file containing commands that Windows can execute. It has a .bat or .cmd extension instead of .txt. When you double-click on it, Windows follows the instructions it contains and displays the result in a black window called Command Prompt (cmd.exe).
No installation is required to create a batch file. By default, Windows includes the command interpreter (cmd.exe) for executing these files. A simple text editor such as Notepad is all you need to write the script.
- Click on Start, type Notepad and open it.
- Enter the following code:
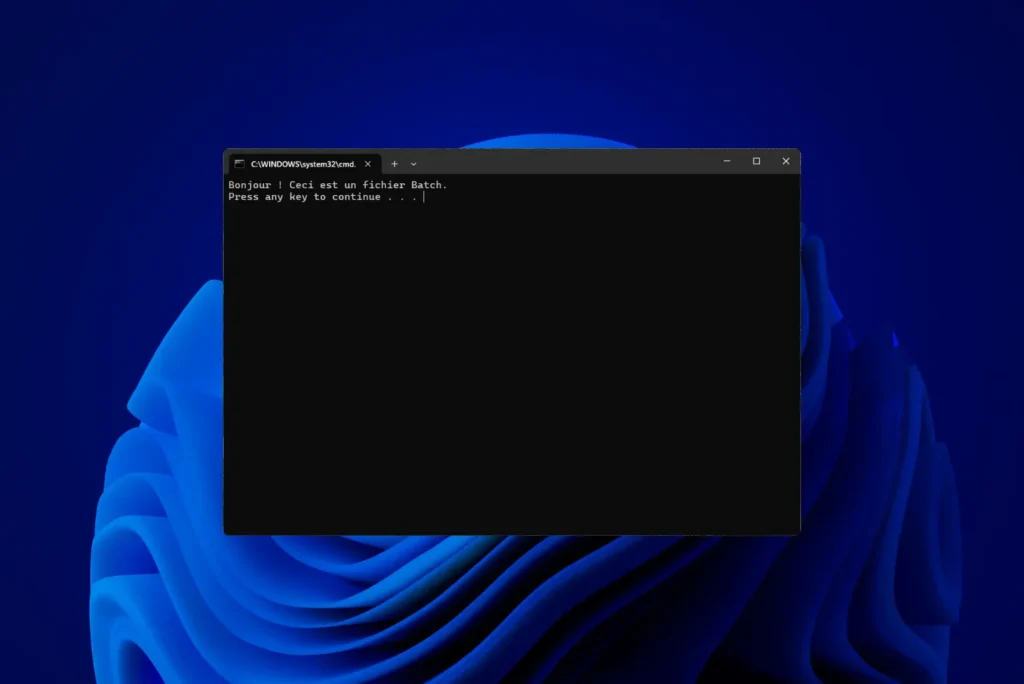
@echo off echo Hello! This is a batch file. pause- Click on File > Save as…
Choose a location (e.g. Office).
- In File name, enter MonScript.bat
- In Type, select All files (.) instead of Text files (.txt).
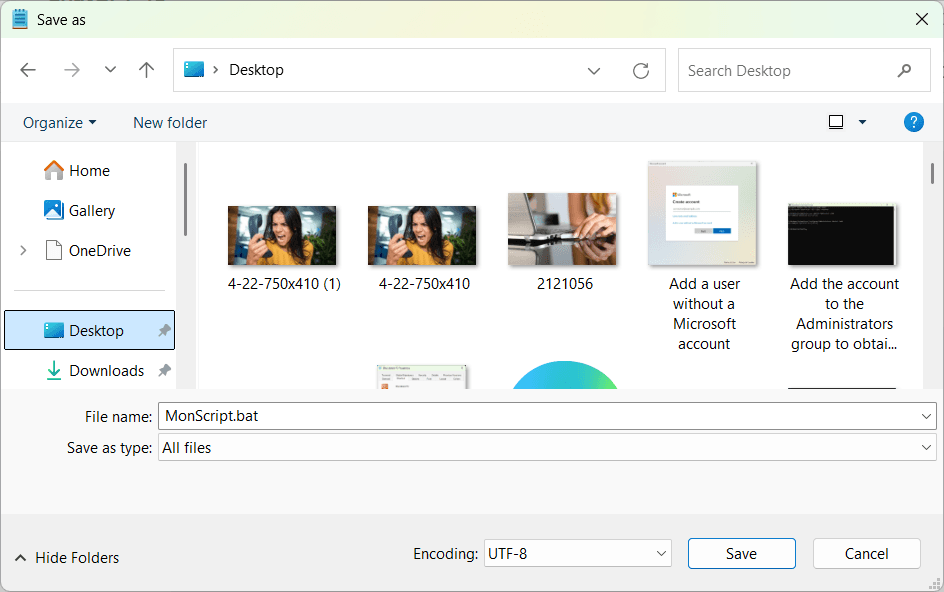
- Click on Save.
🚨 Warning! Don’t put .txt at the end of the file name, otherwise Windows won’t recognize it as a Batch script.
Explanation of code lines:
@echo off: Prevents commands from being displayed, so that only the result is shown.echo Hello! This is a batch file.Displays the message.pause: Pauses the program until the user presses a key.
Run the Batch file
- Go to the location where you saved the file (e.g. Desktop).
- Double-click on MonScript.bat.
- A black window (the Windows Command Prompt) opens, displaying :
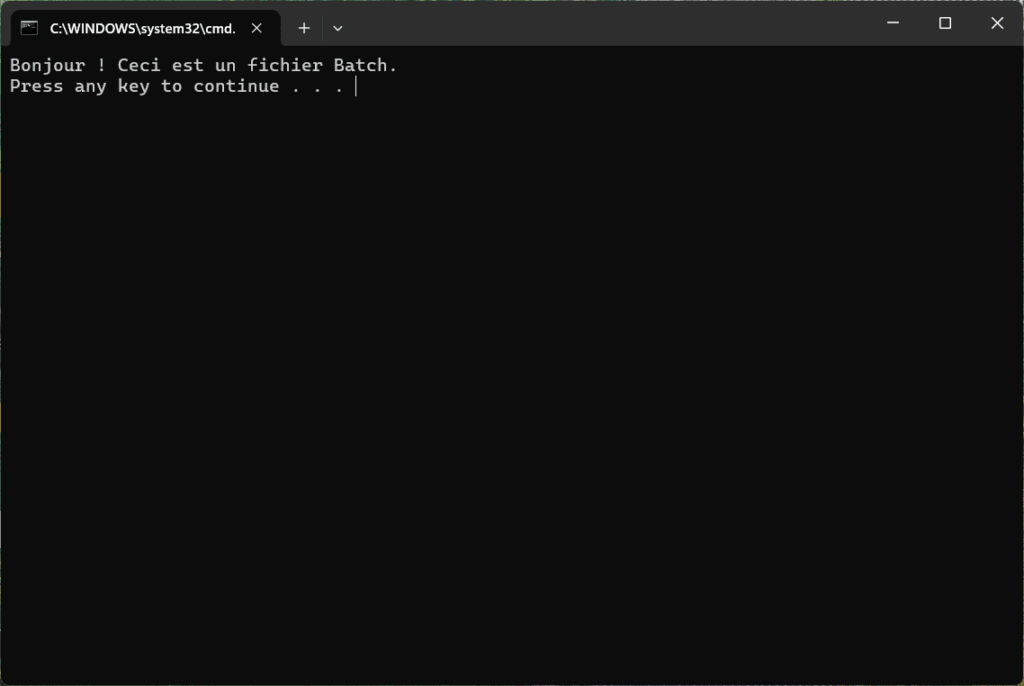
- Press any key to close the window.
🎉 Congratulations! You’ve just run your first batch file!
Batch file example and use case
Batch files are used in many contexts, from personal use to enterprise systems administration. Here are just a few examples:
Automation of common tasks
del /q /s C:Temp*Open several programs with a single command :
start notepad.exe start chrome.exeRestarting a PC after a set time :
shutdown -r -t 60Batch files are a powerful tool for Windows automation, but they also have limitations that may require the use of other languages such as PowerShell or Python.
The main Batch commands for Windows
Some commands require administrator rights to run. To run a Batch file as administrator :
- Right-click on the
.batfile. - Select Run as administrator.
| Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
echo | Displays a message on the screen. | echo Hello, this is a message. |
@echo off | Disables display of executed commands. | @echo off |
pause | Pauses the script until a key is pressed. | pause |
cls | Clears the Command Prompt screen. | cls |
cd | Changes directory. | cd C:Folder |
md / mkdir | Creates a new folder. | mkdir C:NewFolder |
del | Deletes a file. | del C:File.txt |
copy | Copies a file or several files. | copy fichier.txt C:Backup |
move | Moves a file or folder. | move fichier.txt C:NewFolder |
tasklist | Displays a list of current processes. | tasklist |
taskkill | Closes a running process. | taskkill /IM notepad.exe /F |
shutdown | Shuts down or restarts the computer. | shutdown -s -t 60 |
ping | Tests connection to an IP address or site. | ping google.com |
ipconfig | Displays network configuration. | ipconfig /all |
netstat | Displays active network connections. | netstat -an |
tracert | Displays the network path to an address. | tracert google.com |
start | Opens a program or file. | start notepad.exe |
title | Changes Command Prompt title. | title My Batch Script |
color | Changes text and background color. | color 0A |
set | Sets a variable. | set name=Jean |
if | Executes a command conditionally. | if "%name%"=="John" echo Hello John! |
goto | Redirects to a specific section of the script. | goto :end |
exit | Closes the script or Command Prompt. | exit |
The limits and evolution of scripting under Windows
Batch files have long been one of the main ways of automating tasks under Windows. However, as administration and automation needs have evolved, other more powerful and flexible solutions have emerged. These include PowerShell, Python scripting and various third-party tools for automating more complex actions and interacting with the system.
PowerShell: a more powerful alternative to the .bat file
PowerShell is a scripting language and runtime environment developed by Microsoft designed to manage and administer Windows systems in a much more advanced way than Batch files. It’s based on .NET, and allows you to execute far more advanced commands, including :
- Manage Windows updates and system configurations.
- Manage Windows services and processes with
Get-Service,Stop-Process, etc. - Manage files and folders in depth with
Copy-Item,Move-Item,Remove-Item. - Interact with Windows registries and APIs.
- Automate user and group management in a corporate network via Active Directory.
| Criteria | Batch (.bat/.cmd) | PowerShell |
|---|---|---|
| Command complexity | Very limited | Advanced, management of complex structures |
| File manipulation | Basic (copy, move) | Advanced (compression, extraction, content modification) |
| Access to Windows APIs | Impossible | Complete with .NET |
| Security | Low (easily modified) | Better rights management and restricted execution |
| Interaction with the network | Limited | Advanced features (HTTP requests, network management) |